Introduction
The introduction of 802.11b was one of the first major steps towards the expansion of wireless networking – the jump to speeds of up to 11mbps (in reality you would however achieve something like 6mbps) contributed significantly to this. It has since grown and 802.11a and g have been released and are going strong. Because of its proven track record and relatively inexpensive hardware, 802.11b has emerged as a favorite amongst SOHO users. 802.11g has improved on the performance of 802.11b and is backward compatible.
Bluetooth was invented to get rid of wires and can be used to create a Personal Area Network (PAN). It is more of a wireless substitute for connecting devices such as digital cameras, PDAs and mobile phones with each other or a desktop computer. Bluetooth is more suited for connecting two point-to-point devices, whereas Wi-Fi is an IEEE standard intended for networking. Although it has the capability of interconnecting up to 8 devices to form a small LAN, with a low bandwidth of about 700KB/sec and a range of about 30 feet it cannot really be considered as an honorable networking protocol.
802.11b
Wi-Fi (Wireless Fidelity), or 802.11b, is an IEEE standard for wireless Local Area Networks. Backward compatible with 802.11, 802.11b runs on the 2.4 GHz band and is capable of working at speeds of up to 11Mbps. This allows you to surf the Internet at broadband speeds when connected to an access point or in ad hoc mode. The IEEE published 802.11 in 1997 to make it the first globally approved wireless LAN standard. In 1999 they amended the specifications to add two more speeds, 5.5 and 11Mbps.
Out of the 7 layers of the ISO Model (refer to image below), 802.11, like the other 802.x standards, centers around the Physical and Data link layer. Any application, operating system or protocol should work as well on a Wi-Fi LAN as it did on an Ethernet LAN.
An 802.11b wireless network adapter can operate on two modes, Ad-Hoc or Infrastructure. In infrastructure mode all your traffic passes through a wireless access point and can be thought of as a wired network without cables. This is commonly setup to allow resources such as printers and files to be shared. The image below demonstrates such a setup.
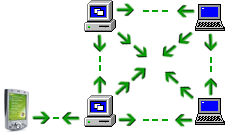
In Ad-Hoc mode, your computers or mobile devices talk to each other directly and do not need an access point. This type of structure can support up to 8 devices connected to each other and is useful when you want to setup a wireless connection quickly or when you have a few computers in your network. The image below demonstrates a typical ad-hoc network.
Advantages
- Interoperability
- Higher data rates (11Mbps)
- Longer range (approx. 100 meters)
- Relatively inexpensive hardware
Disadvantages
- Security
- RF Band is shared
Most new laptops are Wi-Fi enabled and have the technology built in. If they don’t, or you own an older laptop, then you can purchase a wireless NIC card which would fit into an empty PCMCIA slot or USB port (the same goes for Personal Digital Assistants).
Bluetooth
Bluetooth, named after the Danish king Herald Blatand, is a user friendly radio frequency wireless technology initially conceived by Ericsson in 1994. It is a short-range data communications protocol, known also as the IEEE 802.15 standard. A number of large companies, namely Nokia, Ericsson, Intel and Toshiba formed the Bluetooth SIG group in 1998. Since then many other heavyweights such as Microsoft, 3Com, Motorola, and so on have joined and the number of participating companies has now reached 1500.
Bluetooth operates on the unlicensed 2.4 GHz band and uses a frequency hopping spread spectrum technique – which is one of two basic modulation techniques used in spread spectrum signal transmission. Frequencies are switched repeatedly during radio transmission to help reduce unlawful access or other means of telecommunications to cross paths and cause interruption. It also makes Bluetooth communication more robust and secure. Interference from other devices will not cause the transmission to stop, but the speed to be reduced.
Advantages
- Interoperability
- Scalability
- Inexpensive
- Voice/data compatible
- Allows for the formation of an Ad-hoc network
- Low power consumption
Disadvantages
- Short Range
- Low data rate
- RF Band is shared
Bluetooth’s advantage over Infrared (IrDA – Infrared Data Association) is its ability to connect 1-to-many devices rather than 1-to-1. Infrared requires a direct line of sight in order to operate and has a range of approximately one meter. Bluetooth developers have said they did not intend to create an alternative to IrDA but so many companies are now replacing the devices IrDA slot with Bluetooth. Although Bluetooth use is becoming more and more popular and IrDA is being phased out, I do believe that Infrared will, in some way, still be around in the near future.
Bluetooth technology can be found in many devices. Nowadays, if you purchase a laptop, PDA or mobile phone it is bound to be Bluetooth enabled.
Types of Bluetooth Devices
Bluetooth Dongle
Installing a Bluetooth dongle is easy; simply insert the CD that came with it, follow the on screen prompts and then plug the dongle into a free USB port. If you had a Bluetooth compatible laptop you could just plug the dongle into an internet enabled personal computer and check your e-mail, download Windows updates, or transfer files. On the same lines you could also synchronize your PDA with your personal computer and download the latest appointments, e-mails or send text messages.
Bluetooth Headset
Bluetooth headsets are mainly used with compatible cell phones, place the headset on your ear and roam freely while talking to colleagues, friends and family. You could also connect to a dongle on a personal computer and use it for voice conferencing for example. A number of products exist on the market today, which all offer good sound quality and have a similar variety of features. Prices vary depending on manufacturer but usually you can get a decent one for around $75 to $150.
Conclusion
In this article we have learnt how, essentially, Wi-Fi is really for when cabling is not a feasible option and Bluetooth is for intercommunication between devices without the need for a PC.
Bluetooth makes connecting various devices to each other without the need for cables a fairly easy task, whereas 802.11-based products can extend, or replace, a wired Local Area Network. From a personal user’s point-of-view, I would suggest – if possible – having both available if your everyday life requires you to travel to different destinations and meet different people. This way you will always be ready, if one isn’t available then you can use the other.
It’s no secret that the overall performance of a wired LAN is more superior to a wireless network. However, expect improvements, in the coming years things will get bigger and better. Having said this, the word that comes to my mind when I think of wireless – especially Wi-Fi – is Convenience. This technology makes sitting out on the porch or in the garden on a hot summer’s day and browsing the Internet a possibility. Now that is very convenient if you ask me!