Sponsored by Stellar Data Recovery
In Microsoft Exchange, you can create a recovery database (RDB) to recover or restore mailboxes and mailbox items. RDB allows you to mount a backup copy of the mailbox database and extract one or more mailboxes or certain mail items. It is used to perform Dial Tone Recovery for recovering and restoring mailboxes without disrupting the active copy of the mailbox database that is currently running. The downside of this is that you would need plenty of storage space as you’ve to restore the entire mailbox database to just extract a mailbox or a mail item.
A recovery database can be created and accessed by Exchange administrators only to restore mail items and mailboxes from it. You can use any backup copy of the mailbox database stored on the same or another server in the same organization.
In this article, we will discuss the step-by-step procedure to restore an Exchange database to the recovery database for restoring the mailboxes or mailbox items.
Restoring an Exchange database from a recovery database
To restore the Exchange database as a recovery database and extract mailboxes or mail items, the following steps are required:
Step 1: Copy or restore a database and its log files
First, copy the database file with its log files to a location that you are going to use for the recovery database. You may manually copy the files or use Windows Server Backup to restore the backup copy of the database and log files. The steps are as follows:
NOTE: These steps work only if you have created a backup of the Exchange database using Windows Server Backup.
- Launch Windows Server Backup, select the backup, and click on Recover…
- Select This server (SERVERNAME) if the backup is stored on the same server or choose A backup stored on another location if it is stored on another server or storage location. Then, click Next.
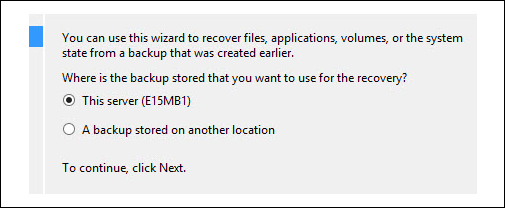
3. Select the latest backup data and time (highlighted in bold), as any email sent or received after the backup date will be lost. Then click Next.

4. Select Files and Folders and click Next to restore the database and log files.

5. From the list, select the database and log files to restore for RDB.
6. Select a location where you want to restore the database and log files backup. You may choose the Original location if you know it or select Another location.
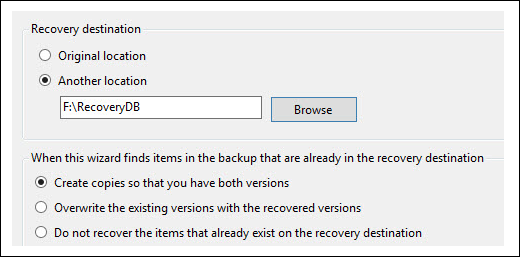
Important Note: No action is required if the .edb and .log files are saved at the same location. However, if the .edb and .log files are located at different locations, you must restore them in two separate processes.
- Confirm your selection and then provide admin credentials.
- Click on the Recover button to start restoring the database.
Step 2: Check database status
By default, the restored mailbox database will be in the Dirty Shutdown state. To check the database status and bring the mailbox database to Clean Shutdown state, use the following commands:
The command below provides the current status of the database.
Eseutil /mh <path to database file>
When the database is in Dirty Shutdown state, it cannot be mounted. To bring the database to clean state, Soft Recovery is required. The command to perform Soft Recovery is as follows:
Eseutil /r E001 /l “C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\Vxx\Mailbox\Logs” /d “C:\Program Files\Microsoft\Exchange Server\Vxx\Mailbox\MyDatabase.edb” /i
Once the command is executed successfully, check the status of the database. It should be in Clean Shutdown state.
Eseutil /mh <path to database file>
In case the database is still in Dirty Shutdown state, you may proceed with Hard Recovery. However, it may lead to data loss as Hard Recovery removes damaged mailboxes and mail items from the database. Hard Recovery should only be used as the last resort. Like Soft Recovery, it isn’t guaranteed that the database will get to a healthy state after Hard Recovery. The command is as follows:
ESEUTIL /P <path to database file>
You may also use a third-party Exchange recovery tool, such as Stellar Repair for Exchange, when Soft Recovery fails and you do not want to risk data loss. The tool can help you export the mailboxes from Exchange EDB to live Exchange directly in a few clicks, without the risk of data loss. In addition, you can open and browse through a mailbox database that is in Dirty Shutdown and without the need for log files.
Step 3: Create a recovery database
Once the database is in Clean Shutdown state, you can use the New-MailboxDatabase cmdlet to create a recovery database. The syntax is as follows:
New-MailboxDatabase -Server StellarInfo -Name RDB001 -Recovery -EdbFilePath “C:\Databases\Recovery\RDB001.EDB" -LogFolderPath "C:\Databases\Recovery\RDB001"
To check if the recovery database is created successfully, execute the following PowerShell command:
Get-MailboxDatabase <RDBName> | Format-List
Step 4: Mount the recovery database
Now you are ready to mount the database for recovery on the server. The command is as follows:
Mount-Database RDB001
Check if the database is mounted successfully by using the following cmdlet:
Get-MailboxDatabase -Status| Format-List name, server, mounted -AutoSize
At this stage, you have successfully restored and mounted the Exchange database. The next step is to extract and restore mailboxes and mailbox items by using the New-MailboxRestoreRequest cmdlet. Once the mailboxes or mailbox items are restored, you can go ahead and remove the recovery database by using the following command:
Dismount-Database RDB001
Type Y and press Enter to confirm dismount. Then delete the database and log files from the disk to free up the storage space.
Restoring Exchange from a recovery database: Wrapping it all up
In this article, we discussed and demonstrated the steps required to restore an Exchange database to a recovery database for recovering individual mailboxes or mailbox items. However, RDB recovery works only if you have a backup copy of the database and are assigned with “Mailbox recovery” permissions. It also requires log files copied to the RDB folder and cannot restore an Exchange server, multiple databases, or recover Public Folders. By using an Exchange recovery software, such as Stellar Repair for Exchange, you can overcome these limitations and restore mailboxes from the Exchange database to PST or export the mailboxes to a live Exchange server directly. This saves time, effort, and avoids any risk of data loss.
Featured image: Shutterstock




how many types failover in exchange server 2016. can explain failover.