Imagine walking along a street and you suddenly get a notification on your phone about an amazing discount offered by a clothing brand. As soon as you take your eyes off the notification, you see the retail outlet of the same brand. Won’t you be enticed to enter the store? This is exactly how proximity marketing works. When you market your business to customers near to you (your retail store, in this case) it is called proximity marketing.
Proximity marketing is like the real-world call-to-action to a digital advertisement. You see the ads in your phone and can immediately take actions in the real world. Proximity notifications are sent to users with technologies like near field communication (NFC), global positioning system (GPS), radio frequency identification (RFID), and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). Each of these techniques belongs to different points in the spectrum of proximity marketing. So let us first understand the marketing funnel before we discuss how these technologies work.
Understanding the ‘marketing funnel’
The marketing funnel has three stages:
- Awareness
- Consideration
- Conversion
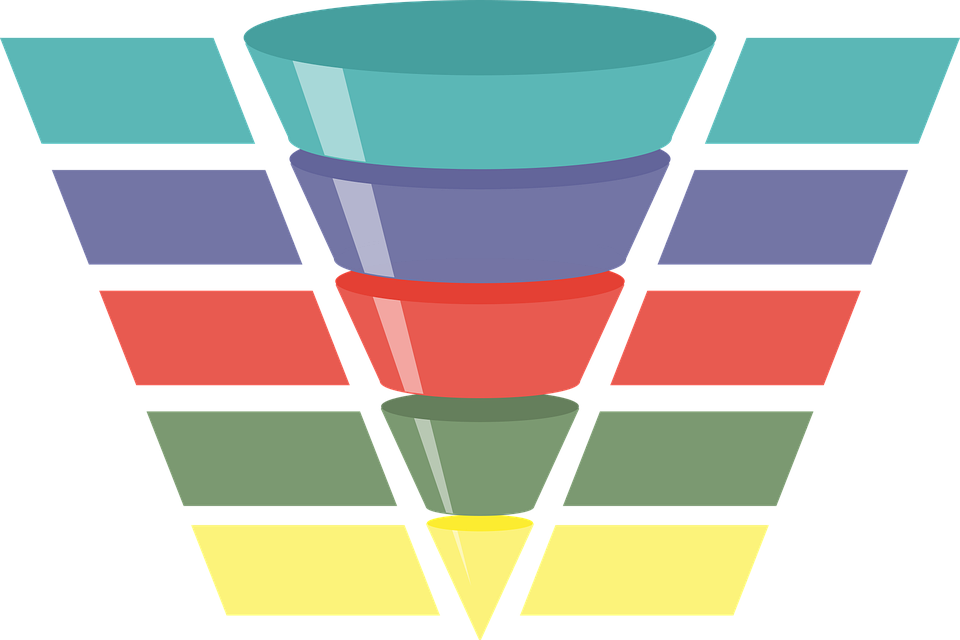
All types of marketing, including proximity marketing, start with lead generation. Lead generation is the process of identifying the people who might be interested in your product. These people are called leads. You attract leads by making people aware of your business. This is called the awareness stage.
Once you generate leads, the next goal is to get your leads to understand the benefits of becoming your customer without pushing them to sales just yet. This process is called lead nurturing. During this process, you will be able to identify who among the leads have the potential to become your customers. These people are called potential customers.
Potential customers already have a need for your offerings. So you don’t have to explain to them about your product, but you should show them how you are better than your rivals. At this stage, you give the potential customers a reason to consider you among the plethora of similar businesses in the market. This is called the consideration stage.
Once you successfully convince your potential customers that you are the best, you can convert them into real customers. This is where the sales happen and this stage of the marketing funnel is called conversion.
Fortunately, proximity marketing technologies can help you at all the three stages of the marketing funnel. Here is how they work.
Near field communication system
What is NFC and how does it work?

As the name suggests, near field communication enables nearby devices (less than eight inches away) to communicate with each other. NFC devices are electromagnetic. When they are brought close to each other, their magnetic fields interfere. The data is transmitted through the magnetic field. This is called electromagnetic induction.
NFC devices can be transmitters, receivers, or both. The devices that can only transmit but not receive are called passive NFCs, for example, NFC ID badges. The devices that can both transmit and receive are called Active NFCs, for example, ID badge readers. Passive NFCs, in general, don’t have a power supply of their own. They are activated when they are brought closer to active NFCs by virtue of electromagnetic induction.
Why is NFC used in proximity marketing?
NFC can be useful in the consideration and conversion stages of marketing. An NFC system works like QR codes because users have to initiate the connection. Today’s smartphones come with an NFC chip embedded in them. Users have to bring their smartphones in proximity to the NFC transmitter in order to receive the messages.
NFC business cards
Traditional paper business cards are a good way of marketing your services but the cards are too small to convey everything that you want to say. Now, with NFC business cards, businesses are able to pack everything they want to convey to their customers in a very efficient manner. All they have to do is just tap the card against their phone to receive a message complete with contact details, or even point them to a web page right on the mobile device. That’s convenient and powerful, and it’s possible with an NFC business card.
Ticket bookings and navigation
In movie theaters, NFC tags are deployed near digital signage. When the customer taps her phone against the signage, the phone displays the online platform to book tickets. Similarly, NFC tags are deployed in billboards and near traffic signals. This way, businesses can help customers get directions to their nearest outlet just by customers tapping their phone against an NFC tag.
Contactless payment
NFC readers make payments easier in brick-and-mortar stores. Payment is instantly made from the customer’s digital wallet by just tapping their phones against the NFC point-of-sale (PoS) devices. Some debit and credit cards are also embedded with NFC chips. All you have to do is just tap your card against the point-of-sale device to make a payment.
Global positioning system
How does GPS work?
GPS works by virtue of a system of 30 satellites around the Earth. They are arranged in such a way that wherever you (and your smartphone) are on Earth, you will intersect the signal range of three satellites. Your location is calculated using the transmission time and your distance from the three satellites. This technique is called trilateration. This calculation is done every billionth of a second and that’s how GPS updates locations at the speed of thought.
Geofencing
Geofencing is a technique where the people in a particular radius are notified with promotional content on their phones. This radius is called a geofence. Geofencing is mostly used by retail outlets and restaurants to target the people in the vicinity of their venues. Whenever somebody enters the geofence with GPS enabled, they get a notification that would entice them to visit the restaurant. This technique is also called radius targeting.
Geotargeting
Geotargeting also works like geofencing except that it can target a particular audience demographic. In geofencing, you just send the same information to all the phones within the geofence, but with geo-targeting, you send different notifications to different people. For example, a hotel offers 50 percent discount on buffets and the bar of the same hotel has a buy-one-get-one offer on liquor. Geotargeting determines the age of the user based on their account information and sends the offer on liquor only to adults.
Geoconquesting
Geoconquesting is a location-based marketing technique where businesses look to attract their competitor’s customers to them. For example, when somebody browses the web for “Coffee Shop A” (which is your competitor), they also get a result that talks about a better offer in “Coffee Shop B” (your business). This way, customers would be more attracted toward yours than your competitor’s shop.
Radio-frequency identification
RFID is similar to the barcode scanners we see in retail stores except that RFID requires the object and the scanner to be in a line of sight. An RFID system usually contains a reader and tag. The reader continuously sends out radio waves looking for an RFID tag. Whenever a tag comes within the range of the reader, it sends a feedback signal. This signal contains some information, in this case, it would be a marketing message.
Like NFC, RFID tags are also classified as active and passive but additionally, RFID systems have another category of tags called the semi-passive tags. Semi-passive tags have their own power supply to activate themselves but depend on the reader’s power supply to transmit data. Here are some applications of RFID in proximity marketing.
RFID in fitting rooms
Apparel stores generally plant RFID tags on their items for security purposes. Some stores have taken it to the next level by leveraging a smart RFID display in fitting rooms. Whenever a customer enters the room with apparel, the RFID tags in the apparel connect to the display and show the customer-related products.
RFID bridges the supply-demand gap
Supplying the demand is as important as marketing. RFID readers can track the movement of each product. RFID tags deployed in warehouses and stores, inform the store managers and manufacturers about the momentum of the products. This helps retailers track which products sell faster than others and which sections need to be restocked more frequently. This helps manufacturers ensure that their items never go out of stock.
Bluetooth Low Energy

BLE has been the most popular proximity marketing technology in recent years. Businesses deploy Bluetooth transmitters called beacons to send notifications to smartphones in the vicinity. The range of beacons can be extended up to 450 meters which is higher than any of the existing proximity marketing technologies.
Most smartphones generally come with built-in protocols to receive beacon notifications. Two of the most famous protocols are Eddystone (a product of Google) and iBeacon (a product of Apple). Businesses use beacons in their stores and public places to reach out to customers. A few restaurants even make their delivery personnel carry tiny beacons in their pocket and keychains to market their products on the go. Here are a few interesting ways how businesses are using beacon technology.
Lift and learn
Lift and learn is common in retail stores. A tiny beacon is attached to every product on the shelf and a smart display is fixed near every shelf. The range of the beacon is adjusted in such a way that the smart display connects to the beacon when a product is taken from the shelf. So whenever a customer picks a product from the shelf, a lot of information about the product is displayed on the digital signage. When two products are picked at the same time, a comparison of the products is displayed.
Omnichannel
Brick-and-mortar stores are extending their business online and e-commerce sites are setting up their retail outlets. Omnichannel is the buzzword among retailers and beacons behave like a bridge that connects the channels. For example, whenever a product goes out of stock in a retail store, a beacon can notify the customers about the availability of the product online along with the link to purchase it.
Proximity marketing: right message, right time
The biggest strength of proximity marketing is its ability to deliver the right message to the right user at the right time. This contextual approach of proximity marketing has made it 16 times more effective than Google Ads. Also, the click-through rates of beacon-based campaigns are significantly higher than that of the popular social media channels. Proximity marketing is also becoming popular among the leading players in the market like Google, Microsoft, Apple, and Qualcomm. The retail industry witnesses the fastest adoption among the 19 industry verticals that have invested in proximity marketing. With proximity marketing technology growing at a CAGR of 30 percent, its global market revenue is expected to surpass $25 billion by 2025.
Featured image: Shutterstock



