For businesses that have questions about using smartphones and tablets as part of their mobility strategies because of worries about security and distracted employees, Google hopes its Android Kiosks will be the answer.
With more than 2.3 billion Android smartphones in use over the globe, Android holds the global mobile market share of more than 75 percent. Given its ease of use, flexibility, level of customization, and lower costs, Android devices are also the choice for many enterprises and organizations. But for many businesses, Androids are not considered secure enough for use in the workplace — or, like all mobile devices, provide too many distractions. Google is trying to undo that perception with Android Kiosks, a mode that promises added security and fewer diversions.
Every company that adopts an enterprise mobility strategy has a specific set of use-cases that they expect their employees to perform from a device. But having too many nonwork features available on the devices can cause a decline in productivity because employees may be wasting time doing other things.

COSU
To deal with this, Google has come up with an intuitive solution in the form of a solution called COSU (corporate-owned single-use). The COSU solution set allows businesses to set up Android devices to fulfill a specific use case. This allows the company to get the most from an Android device while having their employees confined to only specific uses the device can perform.
In our everyday lives, all of us encounter a number of these COSU devices. Just to name a few of the most common COSU use cases: digital signage, taxicab booking, vending machines, inventory management, ticket printing, movie theaters, and parking spaces. COSU allows IT administrators to control all these devices remotely and can lock down the device to a particular usage or a small set of apps. This prevents users from using other applications and performing other actions on these devices.
Android kiosk mode
Android Kiosks are simply the devices that are meant to run a single application and to serve a specific use case. To create or enable a secure kiosk mode in any Android device, a few Android features need to be disabled. For any Android device to work in kiosk mode, it is essential to lock down the device and confine the user to a specific application without the option to close it or switch to another application.
Here are some of the essential requirements needed to run an Android device in Kiosk mode:
- Confining to a single application to serve a specific use case.
- Hiding the navigational button (home and recent apps) in Android.
- Disabling status bar.
- Curbing or blocking all paths to settings.
- Turning off calls/messages as per the use case.
- App to run in a full-screen mode.
Starting from the Android 5.0 Lollipop, Google introduced two ways to lock down an Android device for a single purpose.
App pinning
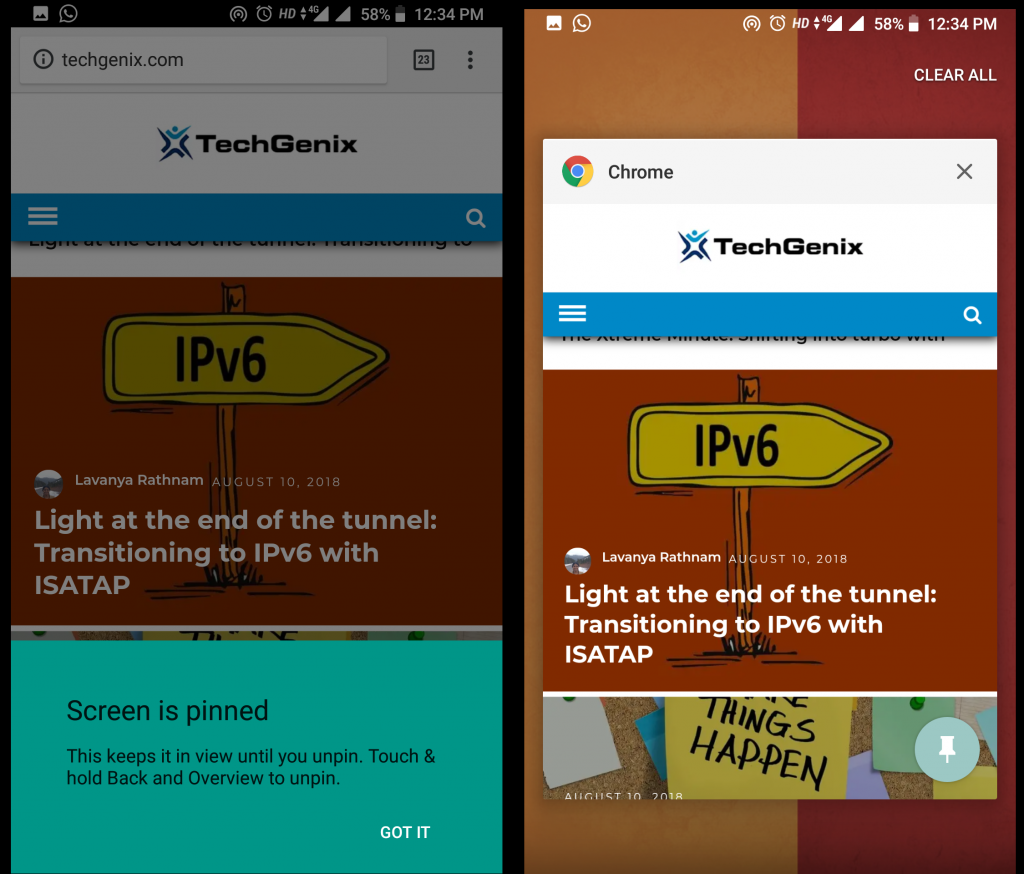
Using the app pinning feature, users can temporarily pin a selected application on the screen. Any app installed in the device can be pinned using this feature. Navigation buttons including the home and recent buttons are visible in app pinning mode but are disabled. Users can exit this mode by long pressing the back or home button.
Lock task mode
Lock task mode is yet another effective way of turning an Android device into a single-purpose kiosk. Lock task mode was introduced in Android 6.0 Marshmallow and using this mode, only applications whitelisted by the Device Policy Controller (DPC) can be locked. Home and recent buttons are hidden in this mode and this mode can be exited by calling stopLockTask() method.
Applications of Android Kiosks
Restaurants
In recent years, restaurants and hospitality chains started investing huge capital in various applications and dedicated devices to automate the process of taking orders, serving food, inventory management, and taking customer feedback. With Android Kiosk, any Android device, which is inexpensive and is readily available, can be turned into a dedicated device to serve the above purposes. Almost all these tasks and other tasks in a restaurant or any hospitality chain can be handled with an Android device.
Transport
Most ride-hailing services such as Uber and other means of transport such as metro systems have started using Android Kiosks in their everyday operations. Every vehicle is provided with an Android device running as a kiosk to facilitate the drivers and the passengers with an easy hassle-free ride experience.
Manufacturing
Every manufacturing unit needs to stay updated in terms of their manufacturing environment and to incorporate the latest technologies. For huge manufacturing plants, replacing the devices can be a heavy cost for companies. Android Kiosks serve as a cost-effective solution that doesn’t need to be replaced when some new technology turns up. The organization just needs to update the application in the devices, which is very pocket-friendly and can be done without affecting the operations.
Information systems

Smartphones and tablets are already the most widely used devices to serve as a medium of information. Use of Android Kiosks to serve as information systems serves the purpose of keeping people updated with the necessary information. Furthermore, locking everything else in kiosk mode can ensure that the device is being used only for the intended purpose.
Apart from these, there are several other use-cases and applications where Android Kiosks are being used. Google has already planned for improvements in Android Kiosks, and accordingly, the new Android P will make it possible for the users to choose a selection of applications to run in kiosk mode. This means kiosk mode will not be confined to a single application. Android P will come with a dedicated launcher showing all kiosk applications.
Android provides many features for developers to create kiosk applications. However, there are several other measures that businesses need to take care of. Encasing the devices to prohibit the use of the power button or adding restrictions to unplugging the power source are two such examples. If built and configured properly, Android devices running COSU applications can prove to be an effective and user-friendly means of running a business with ease and almost negligible maintenance.
Featured image: Shutterstock



