Introduction
A few months ago we looked at the various array options for Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 Enterprise Edition. In this month’s article we will dig a little deeper into one Enterprise array option – the standalone array. We will take a look at how it differs from an Enterprise Management Server (EMS) managed array, and what to do if the array manager is unavailable.
Standalone Array
As I outlined in my previous article, a standalone array is a group of TMG Enterprise Edition firewalls configured as a single logical firewall. In a standalone array, one of the array members is designated as the array manager, and each member of the array will synchronize their configuration with this system. In a standalone array there is no concept of an enterprise. There is no option to configure enterprise level policies or networks, and only a single array with up to 50 members is supported (limited to 8 with Network Load Balancing (NLB) enabled). The standalone array is managed in the same way as a single TMG Standard Edition firewall, with the added benefits of redundancy and high availability provided by NLB, along with centralized configuration and policy management for all array members.
Looking at a TMG Enterprise standalone array in the management console, it appears to be identical to a TMG Standard Edition firewall. As you can see, there are no enterprise-level policies or networks.
Figure 1
In fact, the only indication that this is a TMG Enterprise standalone array is shown when you highlight the System node in the navigation tree and select the Servers tab. Here you will see this standalone array has three members.
Figure 2
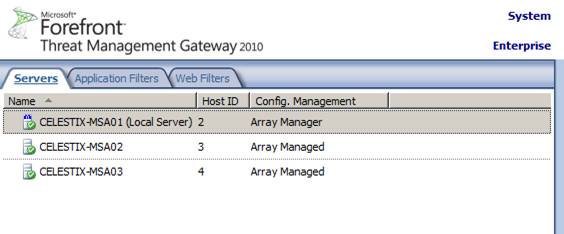
Figure 3
Array Manager
Each member of a standalone array will synchronize their configuration with the array manager. The array manager is created by joining one TMG Enterprise Edition firewall to another. There is no special configuration required to prepare a TMG firewall to be an array manager. In a standalone array there can be only one array manager. This differs from EMS-managed arrays, where multiple EMS can be deployed for redundancy. If the array manager is temporarily unavailable, the remaining array members will continue to function using the configuration they received during their last successful synchronization. During the time the array manager is unavailable, you will not be able to make changes to the array policy or configuration or generate reports. Once the array manager is back online you can continue to manage the array normally.
Changing Array Managers
If the system designated as the array manager becomes permanently unavailable for any reason, it will be necessary to designate another array member as the new array manager. To accomplish this, open the management console on the array member you wish to designate as the new array manager and highlight the root node in the console tree.
Figure 4
In the tasks pane, select Set as Array Manager.
Figure 5
A warning message appears indicating that setting the array manager while another server is already configured as the array manager may result in a misconfiguration. Choose Ok to continue.
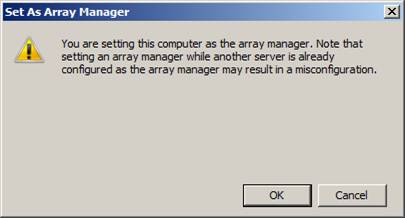
Figure 6
Note:
The process of setting a new array manager when the original array manager is offline can take several minutes.
Once complete you will now see this system identified as the array manager.
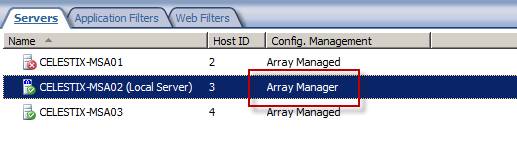
Figure 7
Next you will need to configure the remaining array members to point to the new array manager. On each array member, open the management console and in the tasks pane, select Change Array Manager.
Figure 8
Note:
Opening the management console on the remaining array members may take an extended length of time and appear frozen because the original array manager is offline and cannot be contacted. Be patient. Eventually the management console will open and allow you to specify a new array manager.
Enter the IP address, or preferably the fully qualified domain name (FQDN), of the system you wish to designate as the new array manager.
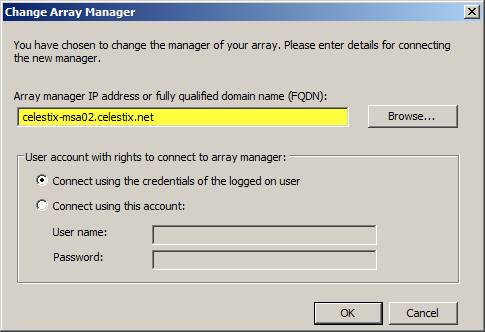
Figure 9
By default, the original array manager is also the report server for the array. For reporting to function properly after changing the array manager, highlight Logs & Reports in the console tree, then select the Reporting tab.
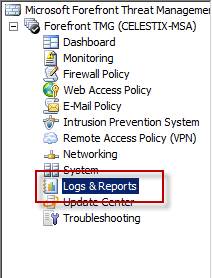
Figure 10
In the tasks pane select Configure Reporting Settings.
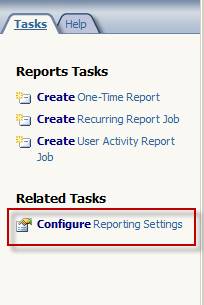
Figure 11
Select the Report Server tab, and then choose another array member to serve as the report server for the array.

Figure 12
Once you have completed these steps you can now you can safely delete the old array manager by right-clicking on the system and selecting Delete.
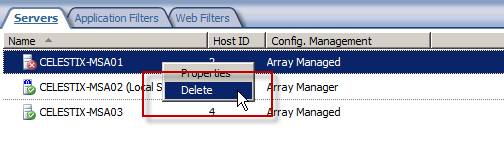
Figure 13
Conclusion
The standalone array feature of Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 is an excellent deployment option for organizations that require high availability for their TMG firewalls, but do not want the additional overhead of configuring a full EMS managed array. The failure of the array manager does not prevent the remaining array members from processing traffic, and with little effort another array member can easily be configured as an array manager without interruption in service.



