With growing cyberattacks and data breaches worldwide, businesses continuously struggle to safeguard their confidential data. These issues cause massive losses to businesses both in terms of reputation and capital costs. Accordingly, cyber protection, especially data protection, is now a top priority for almost all businesses. Data protection prevents the exploitation of sensitive information and can also prevent fraudulent activities such as hacking, phishing, and identity theft. One example of a data protection solution is data masking.
In this article, I’ll define data masking, and show you its benefits, types, techniques, best practices, and challenges. Let’s begin.
What Is Data Masking?
Data masking is a method that replaces the original data with a structurally similar pseudo version of that data. It basically hides sensitive info to protect your data.
This protection method primarily aims to create a functional dataset that can help businesses carry out regular operational activities without risking privacy or loss of confidential information.

As the name suggests, data masking is an umbrella term that refers to any form of masking. This includes data obfuscation, anonymization, scrubbing, and de-identification. This creates a working version of data that’s ultimately indecipherable. In turn, a cyberattacker won’t be able to reverse engineer this “masked” copy to find the original data.
Let’s now look at some of the benefits of utilizing this data protection mechanism.
Why Should You Mask Your Data?
Data masking enables you to carry out regular business activities without compromising or risking the loss of confidential information. But it also has several other benefits. Here are some of them:
- Protects any Personally Identifiable Information (PII), which is very important for every business
- Enables you to build an organizational security policy that’s compliant with several regulations and policies such as GDPR and HIPAA
- Fits the masked data in a structured manner to enable you to carry out several operations such as testing, demos, and more
- Prevents cyberattacks like data and identity thefts, service hijacking, insider threats, and phishing attacks
- Provides access to data for operational teams like development and sales without risking theft or exposure
- Reduces risks associated with new service adoptions and migrations
Now that you understand the benefits of data masking, let’s look at its different types.
4 Types of Data Masking
You can mask your data in many ways. And depending on your needs, you can choose any of the below-mentioned types for your business:
1. Static Data Masking (SDM)
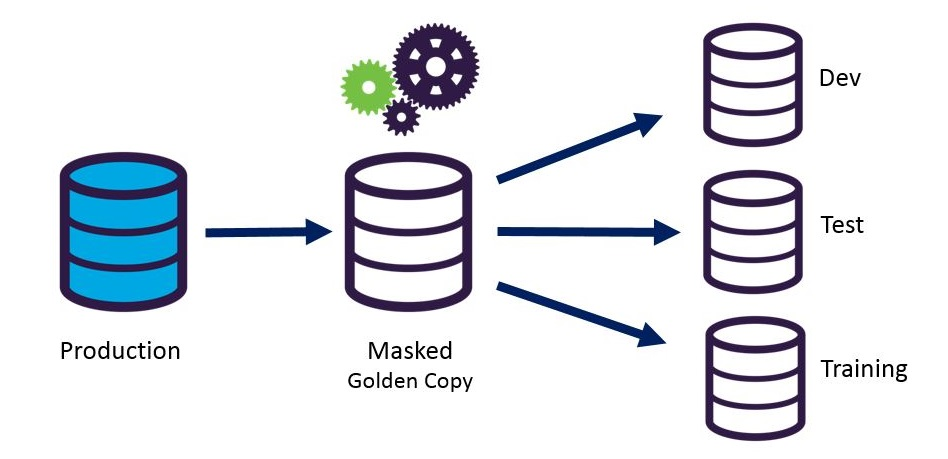
SDM creates a full copy of the production database with fully or partially masked information. This duplicated and masked data is now copied to different environments like tests or development. This way, the organization can use and pass the data on to downstream services or external vendors if needed. Using SDM, you can create a sanitized copy that masks any sensitive information.
2. Dynamic Data Masking (DDM)
Unlike SDM, DDM doesn’t involve second data storage to create a duplicate dataset containing masked information. Instead, it streams data directly from the original database where the original unmasked data resides. Upon request and/or when needed, data gets masked and sent out to downstream services or external vendors.
3. Deterministic Data Masking
This method takes two identical data sets containing the same data types and maps them. This way, it can always replace one value with another. For instance, consider a database with multiple tables, each with a column for first names. This method will replace each of these first names with a fixed replacement. For example, the name “James” will always be replaced with “Smith”.
4. On-the-Fly Data Masking (OFDM)
As the name suggests, OFDM occurs when the data transfers from the original production database to different environments like tests or development. OFDM is ideal for businesses and organizations that are fast-paced, agile, and perform rapid continuous deployments.
Now, let’s analyze the different techniques you can use to mask your sensitive data.
Data Masking Techniques
Depending on how you want to mask your data, you can choose from a variety of techniques to protect your organization’s sensitive information. Below are some of the most commonly used techniques globally.

Data Scrambling
Data scrambling is one of the most rudimentary techniques, which is simple to implement. In this approach, every data character gets rearranged in a random order to replace the original content. For example, if the data contains an ID number (54435), the masked data after applying data scrambling might be 34545.
This technique, however, isn’t very secure. Anyone can decipher the original data from the masked data without external references. Additionally, data scrambling only applies to specific data types like strings.
Nulling Out
Nulling out is another easy-to-implement technique. Basically, the technique completely nullifies certain data rows or columns. This helps keep out unauthorized users. However, this technique isn’t ideal for downstream business activities because certain data is nullified. This technique can also reduce your data’s integrity, so keep that in mind if you implement it.
Value Variance
Value variance replaces the original data value with a function, such as the difference between two data entities. For instance, you can replace the age value in a table containing user information with the age range. This technique preserves the format of the datasets, and you can use it to mask PII.
Data Encryption
This technique encrypts data using an encryption algorithm. Typically, it’s one of the most robust and secure forms of data protection. The data receiver won’t be able to access the data without the decryption key. However, this technique is also complex to implement and requires heavy computing depending on the frequency and amount of data.

Data Substitution
This easy-to-implement technique involves substituting your data to safeguard the original data. The data that gets substituted is usually of the same format, which is a fake yet realistic substitute of the original.
Data Shuffling
Data shuffling is similar to the previously mentioned data substitution and scrambling approaches. This technique shuffles original data with a substitution dataset derived from the same dataset. An example would be shuffling employee names around in an employee dataset. This process preserves the anonymity of the PII to an extent It can also serve as a dataset for downstream services like testing and development.
Pseudonymization
Pseudonymization is a relatively new and modern technique introduced in the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). As per GDPR, pseudonymization is the use of any of the data masking techniques mentioned above, including encryption and/or hashing, to protect personal data.
Depending on your needs and requirements, you can choose any of the techniques above to safeguard your data. You can also choose to implement a hybrid approach. In this approach, you can adapt a simple data masking approach for your less sensitive data and use data encryption to preserve your confidential information.
Next, we’ll take a look at some best practices to help you choose the right protection approach for your business.
Data Masking Best Practices
So far, you’ve learned a lot about data masking. However, you can’t get far without learning about some best practices and how to apply them when protecting your data. I’ll cover those now.
Categorize Your Data
Before implementing techniques to secure your data, you must understand this data. Some techniques, like encryption, can be very computationally and cost-heavy to implement. Therefore, you need to categorize and identify your data to secure it. Remember, you don’t have to mask all your data!
Build Your Own Data Masking Stack
You must identify the level of security you need to implement on the categorized data. For any company, it’s ideal to have more than one technique depending on the need and use for the downstream services. Defining your own masking stack that contains more than one technique benefits you and your business.
Develop Data Masking Templates
You can develop and build your own data masking templates. This way, you can reuse your templates your organization generates new data. This saves time and effort while enabling homogeneous and easy-to-maintain data security.
Educate Your Employees
Human errors are one of the most common causes of cyberattacks and data theft. You must educate your employees on data usage, the necessity of protecting their information, and ensuring its integrity while consuming the data.
Secure the Data Masking Algorithm
It’s your responsibility to secure your data masking algorithms and decryption keys. If you’re implementing techniques such as data encryption, substitution, or shuffling, you should safeguard this information.
We’re almost done here, but let’s first look at some challenges your business might face when implementing data masking.
Data Masking Challenges
Data masking techniques can be a key to securing your data from theft and corruption. However, you’ll need to consider some challenges before implementing one or several of these techniques. Here are some of them:
- Pre and post-data masking format preservation. It’s important to preserve data formats to retain the original data, especially in the event of a disaster or cyberattack
- Semantic integrity. This is yet another common challenge many businesses face, as some techniques can render the data useless
- Uniqueness retention. This can create processing and storage overhead
- Additional data stores. You may need additional data stores when masking your data
- Cost and compute-heavy process. This means you’ll need a robust strategy before implementing most techniques
Let’s have a quick recap.
Final Words
Data masking can be a line of defense against the number of growing cyberattacks and data thefts. This protection mechanism comes in many types, so it’s suitable for all businesses working with sensitive data.
Remember, you need to consider your business’s needs and requirements before choosing one or several of the techniques discussed above. Also, pay attention to the challenges you might encounter along the way and act accordingly.
Do you have more questions about data masking? Check out the FAQ and Resources sections below!
FAQ
What is PII?
PII (Personally Identifiable Data) refers to any information or data that can help identify an individual. Data masking techniques can help you secure your employees’ and customers’ PII.
What are the disadvantages of using data masking?
Although data masking can protect your data from several cyberattacks, you have certain disadvantages. That includes loss of data structure and data integrity, as well as cost and operational overheads.
What are some of the data masking services available in the market?
Although you can implement data masking without the need for a tool or service, you have a variety of readily available services that you can leverage to secure your data. Some of them include K2View, DATAPROF, IRI FieldShield, and Delphix.
What are some of the cyberattacks targeting data?
Some major cyberattacks involving data theft or corruption include malware attacks, phishing, password attacks, man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, insider threats, cyberstalking, and crypto-jacking. Data masking can enable you to protect your data against a majority of these attacks if implemented correctly.
What is data encryption?
Data encryption is a security measure used to safeguard the original data (plain text) by converting it to ciphered (encrypted) text. You can only access the encrypted information by decrypting the data using the specific public and private keys used during encryption.
Resources
TechGenix: News
Explore all the latest news and announcements in the IT enterprise world.
TechGenix: Article on Security and Compliance
Explore everything that you need to know about email security and compliance.
TechGenix: Article on Data Governance, Risk, and Compliance
Learn more about governance, risk, and compliance and their importance.
TechGenix: Article on Data Management Challenges and Opportunities
Discover some of the key data management challenges and opportunities for your business.
Microsoft: Article on DDM
Learn more about Microsoft’s take on DDM.



