Let’s begin
Before we start using ESEUTIL and ISINTEG ensure the following:
- Make a backup of your Exchange databases even if you think the files are damaged and lost.
- Use ISINTEG and ESEUTIL with some understanding about what these tools really do.
- Ensure that you have done all other tests before you use ESEUTIL and ISINTEG.
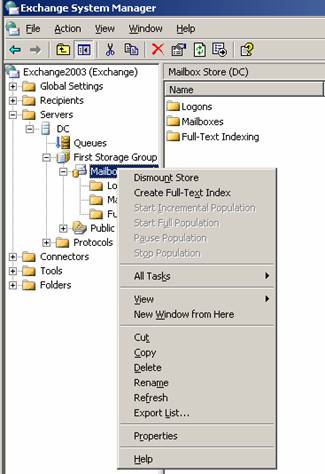
- Dismount the store (then it is accessible for offline defrag, tests and more).
Figure 1: Dismount the information store
ESEUTIL
ESEUTIL is a tool to defragment your exchange databases offline, to check their integrity and to repair a damaged/lost database.
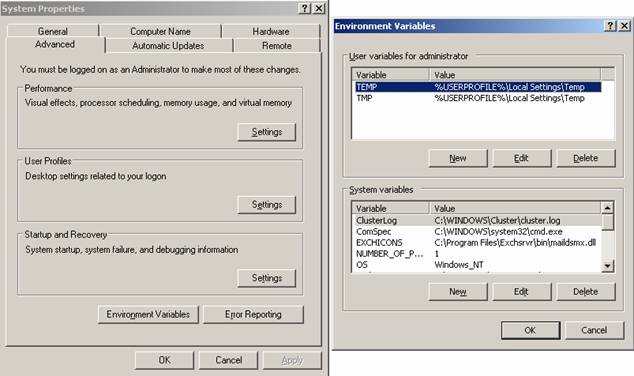
ESEUTIL is located in the \EXCHSRVR\BIN directory. This directory is not in the system path so you must open the tool in the BIN directory or enhance the system path with the \EXCHSRVR\BIN directory.
Figure 2: Change the system path to point to the \EXCHSRVR\BIN directory
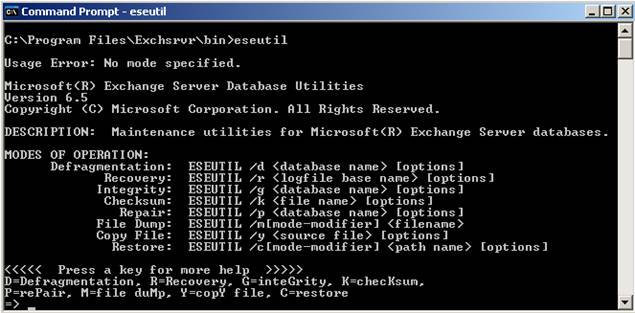
ESEUTIL /D parameters
Figure 3: ESEUTIL parameters
Defrag
Exchange 2003 defragments the Exchange database every night. But this is only an online defrag of the database. An online defrag doesn’t reduce the size of the information store. To reduce the size of the databases, you must use an offline defrag.
When should I use an offline defrag?
Under normal conditions you don’t need an offline defrag, but when you add tons of new users due to a merger or aquisition or when you delete many objects from the store it can be necessary to do an offline defrag.
You can do a space dump with ESEUTIL /MS to determine the space. Also ensure that you have 110% free diskspace associated with the Exchange database size.
Figure 4: ESEUTIL /MS
ESEUTIL parameters for defragmentation
Figure 5: ESEUTIL Defrag parameters
Depending on the size of the information store and your hardware, the defrag process can consume a lot of time.
Figure 6: ESEUTIL defragmentation status
Check the integrity of the Exchange database
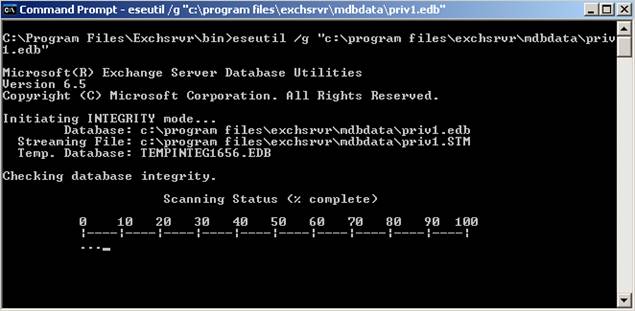
You can check the integrity of your Exchange database with ESEUTIL /G.
Please read NOTE 1 carefully in the following screenshot.
Figure 7: ESEUTIL integrity check
To start the integrity check for the PRIV1.EDB database, type the following command:
ESEUTIL /G „C:\Program files\exchsrvr\mdbdata\priv1.edb“
Figure 8: ESEUTIL integrity check status
Disaster recovery
With a good backup in hand and Exchange databases and logfiles on different hard drives, it is no problem to recover from an Exchange disaster.
Just restore the data from backup and initiate a roll forward of the transaction logs. Well done, the Exchange information store goes online.
But what should you do when your backup isn’t readable or you don’t have a backup? Here’s how these tools come to play.
Before you start:
- Make sure that the databases are really not startable
- Check the Application log for Exchange events that can tell you the cause of the failure
- Make a backup of the database
- Restart the server so that a soft recovery can be done
ESEUTIL /P parameters
ESEUTIL /p repairs a corrupted or damaged database. Ensure that you have a minimum of 20% free disc capacity in association to the Exchange database size.
Figure 9: ESEUTIL repair modus
Example:
ESEUTIL /P „c:\program files\exchsrvr\mdbdata\priv1.edb“ /Se:\exchsrvr\mdbdata\priv1.stm /Te:\tempdb.edb
This command will repair the database PRIV1.EDB. If you have no .STM file, you can create one with ESEUTIL /CREATESTM. Read more about this here.
After running ESEUTIL, you can open a detailled logfile called >database<.integ.raw to see the results.
As a last Step run ISINTEG –fix -test alltests. You can read more about ISINTEG later in this article.
ISINTEG
ISINTEG is used to do some tests on your information store and to fix some detected errors and problems.
Figure 10: ISINTEG parameters
ISINTEG is the only repair utility that understands the Exchange database as an Exchange database.
What does this mean? ESE is a generic database engine that can be used by different applications (Exchange, Active Directory).
ESEUTIL looks into the database as just another ESE database, and can see their tables and indexes. ESEUTIL just fixes the database tables.
Now it is time for ISINTEG. ISINTEG is aware of the relation between database tables and records that turn them into folders and messages.
After you run ISINTEG –FIX, you will see many warnings but you can safely ignore these messages. You should only pay attendtion to the end of ISINTEG. There should be zero errors reported. If there is an error, run ISINTEG again.
This example shows ISINTEG –test folder
Figure 11: ISINTEG –test folder
Conclusion
ESEUTIL and ISINTEG are two powerful tools for ensuring the health of your Exchange information store and a good resource to recover from failures in the store.
Use these tools with caution when you want to repair your information store. It is always a good idea to make a backup before you use ESEUTIL to repair your Exchange databases.
In this article I have explained only a few features of ESEUTIL and ISINTEG. For a full understanding of these tools, read the following KB articles.
Related Links
ESEUTIL
Repairing Exchange databases with ESEUTIL – when and how?
http://blogs.msdn.com/exchange/archive/2004/06/18/159413.aspx
In Exchange 2000 Server and Exchange Server 2003 Eseutil in Repair/Integrity Mode Incorporates /X and /V Options
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;232734
Use the Eseutil Utility to Detect File Header Damage in Exchange 2003
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;825088
How to maintain your Exchange database after you repair by using the Eseutil /p tool in Exchange Server 5.5, in Exchange 2000 Server, and in Exchange Server 2003
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;812357
How to use Eseutil to test transaction log files for damage in Exchange 2000 Server and in Exchange Server 2003
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;248122
Use the Eseutil Utility to Perform a Checksum Procedure on a Streaming File
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;823167
How to defragment with the Eseutil utility (Eseutil.exe)
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;192185
How to run Eseutil on a computer without Exchange Server
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;244525
Eseutil /d Defragments the Database and the Streaming File
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;254132
How to re-create STM File in Exchange 2000/2003
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;555146
How to defragment Exchange databases
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;328804
ISINTEG
Running Isinteg -patch Is Not Needed in Exchange
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;240202
The Exchange Information Store service may stop responding when you run the Isinteg utility in Exchange Server 2003
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;en-us;870976