In the first part of this series, we looked a bit into the Google Cloud Platform, its underlying infrastructure, and different security measures that Google has taken to safeguard data and applications.
In this concluding part, let’s take a deep look into how G Suite works as well as some successful case studies.
What is G Suite?
G Suite is a set of intelligent apps that sit on the Google Cloud Platform. It helps you to do a ton of things such as:
- Create documents, spreadsheets, and presentations from anywhere.
- Collaborate and share documents easily with colleagues and customers located in any part of the world.
- Real-time access where two or more employees get to work together on the same document at the same time.
- Machine intelligence is built into G Suite to handle routine tasks like formatting a presentation or scheduling a meeting.
- Supports encryption at rest and encryption in transit to give the best possible security for your documents.
- Gives better control and monitors access through its granular capabilities.
Besides the above features, G Suite taps into the power of Google’s infrastructure. Whether it’s global distribution, security, or scalability, G Suite gets all this and more from the underlying GCP. To top it, you even get credits and rewards for using certain GCP services through G Suite.
G Suite architecture
Since G Suite sits on the GCP, it has access to components such as the Compute Engine, Security, Storage and Databases, and BigQuery.
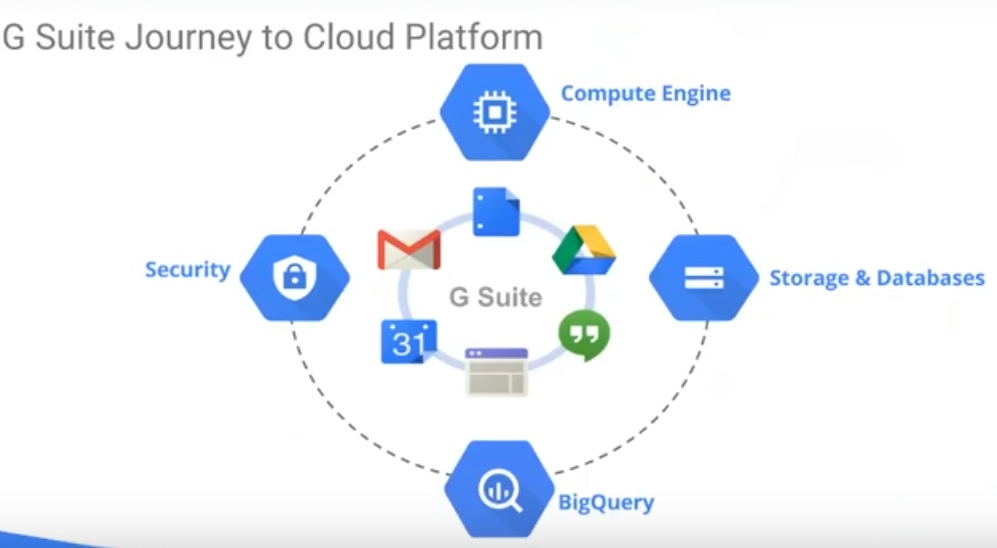
At the webinar, Cloud Customer Engineer Collin Frierson focused heavily on BigQuery because he wanted his audience to understand one of the distinguishing features of G Suite, which is to get the right data insights.
Today, every organization wants to provide personalized services and products to each customer by understanding their needs and expectations. To do this, organizations collate data from different sources, analyze them for patterns, and get insights on their focus areas.
When it comes to G Suite, BigQuery is the way to get these insights. So, let’s now see a little bit about BigQuery, what it is, and how you can leverage it.
BigQuery
BigQuery is one of the first GCP products that was commercially available, and it continues to be one of the most popular products on this platform.
One of the high points of BigQuery is that it allows you to work in a high-scale and high-performing environment, so you can be assured of your application’s uptime and performance. Another aspect that distinguishes BigQuery from its competitors is its high elasticity. This means you can change the type of datasets you want to load to the data warehouse without interrupting existing workflows. This is a convenient feature that makes it possible to get more work done in the same time.
Its computing power, too, is one of the best in the industry. Google, for example, uses BigQuery to compare its log files. To give you a perspective, Google has to sift through hundreds of thousands of log files each day to get meaningful insights about their platform, products, and more. The fact that Google is able to use BigQuery effectively reflects the easy-to-use environment it offers for comparing and understanding vast amounts of data.
Other key aspects of BigQuery is that you can use standard SQL for querying and you can use ODBC connectors to move your data to the BigQuery data warehouse.
It scores high on security and cost effectiveness as well. You’re billed only for the number of seconds your query runs, and this means, the cost will be little to nothing when compared to setting up and running queries on your own infrastructure. In terms of security too, Google uses a strict identity access and management system to protect your sensitive data from unauthorized access.
However, the downside is that BigQuery can’t give you visualizations by itself, and this is why Google has developed a tool called Data Studio. This tool takes data from multiple sources including BigQuery and creates visualizations of what you want. In other words, it collates data from different places and puts them in the form of a graph or chart that is visually appealing and easy to understand.
After going through the different aspects of G Suite, Frierson moved on to talk about some case studies. He specifically explained how some companies were able to leverage the power of GCP and G Suite to transform their businesses.
Let’s look at each case study briefly.
University of Colorado, Denver
The University of Colorado, Denver tapped into GCP for its genomics research. It was looking to create treatment for individuals with specific genetic disorders. For this, they had to analyze massive datasets, some to the tune of petabyte-sized queries.
The system that they had in place took about six to 10 hours to run these queries, but with BigQuery, the same could be done in about 15 minutes. This is because BigQuery was able to take advantage of Google’s phenomenal infrastructure.
The best part is everything was managed by Google, so all that the research team had to do was run their queries and get the results. It was that simple.
Evernote
 Frierson opined that Evernote is one of the biggest success stories of G Suite and the GCP. When this company decided to move to the cloud, it had to migrate billions of notes along with attachments in many notes.
Frierson opined that Evernote is one of the biggest success stories of G Suite and the GCP. When this company decided to move to the cloud, it had to migrate billions of notes along with attachments in many notes.
With Google’s help, it was done within a mere 70 days with no interruption to customers in any way. As a bonus, Evernote was able to get additional analytics that provided insights into its operations.
Airbus
Airbus had a unique problem. It wanted to remove clouds from satellite images to get a better idea of snow-capped mountains. These mountains tend to be at a higher altitude when compared to mountains that don’t have snow caps, so differentiating these mountains from clouds was absolutely imperative for the aircraft’s security.
For this, Airbus tapped into Google’s machine learning capabilities, something that’s built into GCP and is available for G Suite and other applications that sit on it.
This case study goes to show that it’s not just virtual machines and storage, but you can choose to use a whole suite of services including Google’s machine learning APIs.
Snapchat
Snapchat is another success story of Google’s infrastructure. This popular social media platform is built wholly on the Google App Engine and the entire infrastructure is maintained by Google. Snapchat doesn’t own or manage any infrastructure, thereby leaving it free to handle its core business.
With billions of videos and hundreds of thousands of users, Google platform supports it all for Snapchat.
Pokemon Go

This is another interesting case study and also a challenging one, according to Frierson. Pokemon Go built a microservices architecture using Kubernetes and came to Google for scalability.
The estimates were drawn and Google made the necessary resources ready for operations. But the wild success of Pokemon Go was something that neither Google nor Pokemon anticipated, and this meant that there was 50 times more cloud datastore transactions than what they had planned.
Since Google has a virtually unlimited computing and storage power, it was able to add on more resources as traffic grew. Frierson believes this was a great learning experience for Google engineers and since then, they have added more things to Kubernetes.
Spotify
Using GCP allowed Spotify to innovate in its operations. One of its main selling points is the personalized music it offers to its users, so BigQuery was a natural move for this company.
GCP helped to reduce their data processing time from hours to minutes and at the same time, was able to get better insights about the musical preferences of its users, especially in terms of speed and accuracy. This helped Spotify make music-related decisions in real-time to give users a unique experience.
After discussing these case studies, Frierson and Google Cloud Sales Manager Vincent Wienczorkowski answered a few questions from users, and in this section, they gave a brief glimpse into what we can expect from G Suite and GCP over the next few months. Some of them are:
Org Node
Google has introduced an org node to manage cloud projects efficiently. This feature brings the centralized management of all GCP products under the G Suite admin console for better control. The best part is it doesn’t interact with the projects directly, but gives visibility to the organization, and makes it easy for you to do things like centralized billing.
Identity Aware Proxy
Identity Aware Proxy or, IAP, creates a proxy between the Internet and your internal application to give you an extra layer of security. In IAP, Google handles the authentication while the proxy validates it automatically. This way, you’ll have nothing much to do while your product gets more security than before.
Stack driver integration
Stack drivers are integrated to all products in GCP, so you have enhanced functionality like monitoring and availability tracking. Charts and graphs are available in this engine, too, so all this together gives you improved reporting and alerting features.
Overall, this webinar brought out a lot of interesting details about GCP, Google’s underlying infrastructure, G Suite, and more. Both Frierson and Wienczorkowski gave precise and relevant information that the audience could relate to. In fact, such information is sure to help many people like you make more informed decisions with respect to your operations, security, collaboration, and more.
A peek into the future along with new features was particularly insightful as it can help you to plan your cloud adoption and integration better.
Armed with such information, what do you think of the G Suite? Would you be willing to try it out? Please share your thoughts in the comments section.



