Exchange Server 2007 is more than an e-mail system. Exchange Server 2007 has several functions, from e-mail messaging, calendaring and real time collaboration to Unified Messaging. All these Exchange components must work together and several components from Exchange also rely on a lot of Windows Server components like DNS, Active Directory and IIS.
The following picture shows the Exchange Server 2007 core services, but there are more Exchange related services like:
- WWW Publishing Service
- RPC (Remote Procedure Call)
- Windows Management Instrumentarium …
and many more.

Figure 1: Exchange core services
Service dependencies
Many Exchange 2007 services have dependencies on other Exchange and Windows services. You can see the dependencies in the properties of the specific service or in the Registry under:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSet\Services\Servicename
The following picture shows the dependencies of the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service, one of the Exchange Server core services.

Figure 2: Exchange Service Dependencies
Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service (MSExchangeADTopology)
The Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service and provides Active Directory topology information to several Exchange Server components. This service uses DSACCES to provide faster access to Active Directory information.
Microsoft Exchange Information Store (MSExchangeIS)
The Microsoft Exchange information Store service is responsible for handling the Exchange database and providing access for messaging clients like Outlook 200x. The Microsoft Exchange Information Store service has no dependencies on other Exchange services.
Microsoft Exchange Mail Submission Service (MSExchangeMailSubmission)
The Microsoft Exchange Mail Submission Service is responsible for the communication between the Exchange Server with the Hub Transport Server role and the Mailbox Server role. This service informs the Hub Transport Server when new messages are in the Outlook clients’ Outbox. The Hub Transport Server picks up this message and is responsible for relaying and other tasks (Transport rules, Message Records Management etc.). The Microsoft Exchange Mail Submission Service depends on the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service.
Microsoft Exchange Replication Service (MSExchangeRepl)
The Microsoft Exchange Replication Service provides log shipping functionality for Local Continuous Replication (LCR) or Cluster Continuous Replication (CCR) when one of these new technologies in Exchange Server 2007 is activated. The service depends on the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service.
Microsoft Exchange Transport (MSExchangeTransport)
The Microsoft Exchange Transport service is the new SMTP service in Exchange Server 2007 which does not depend on the underlying Windows Server / IIS technology. The service depends on the Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology service.
Microsoft Exchange Transport Log Search (MSExchangeTransportLogSearch)
The Microsoft Exchange Transport Log Search allows administrators to query Message Tracking logs and Transport logs. It also provides support for Transport Pipeline tracing. The service has no dependencies.
Web Services and Exchange 2003
Exchange Server 2007 uses some parts of the Windows Server 2003 Internet Information Services (IIS) infrastructure for Exchange services like Outlook Web Access (OWA) and services like POP3 and IMAP4. Exchange Server 2007 is the first Exchange Server which has no dependencies on IIS 6.0 for the Windows built in SMTP service. Exchange Server 2007 uses its own SMTP stack.
Because Exchange Server 2007 does not provide OMA (Outlook Mobile Access) support, there is no OMA Application pool in IIS and the only Exchange Application pool in Exchange Server 2003 has been divided into five Application Pools in Exchange Server 2007:
- MSExchangeAutodiscoveryAppPool
- MSExchangeOWAAppPool
- MSExchangeServicesAppPool
- MSExchangeSyncApp
- MSExchangeUMAppPool
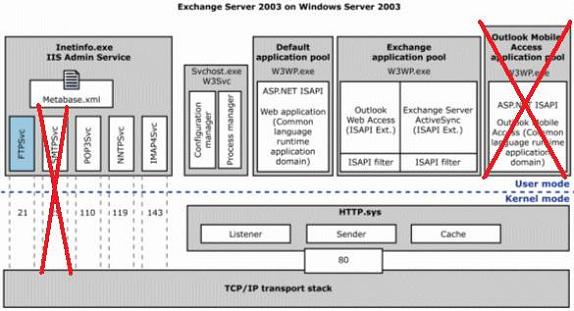
Figure 3: Exchange Server integration into IIS
As you can see in Figure 3 Exchange uses some IIS Application pools and messaging services like IMAPSVC under the control of INETINFO.EXE. HTTP.SYS is the IIS core component which controls a lot of related IIS components.
Note:
Exchange Server 2007 does not need an installed Windows NNTP service. You must uninstall the NNTP service before installing Exchange Server 2007.
EXIFS – not used in Exchange Server 2007
Exchange Server 2007 does not support ExIFS, the Exchange Installable File System, because it is no longer necessary. The Microsoft Exchange Information Store (MSExchangeIS) only uses EDB format databases. The streaming media format (.STM file extension) has gone in Exchange Server 2007. It is no longer possible to mount the Exchange Information Store with this virtual file system driver (\\.\BackofficeStorage in Exchange Server 2003 and 2000).
System Attendant – no longer as powerful in Exchange Server 2007
The Microsoft Exchange Server System Attendant is no longer the most powerful service. The Microsoft Exchange SA provides monitoring, maintenance, and directory lookup services for Exchange Server 2007. This service depends upon the following services: Event Log, NTLM Security Support Provider, Remote Procedure Call (RPC), Server, and Workstation but no Exchange Server service depends on the MSEchangeSA service. MSExchangeSA is responsible for:
- DSAccess (DSAccess.dll) – Provides Exchange Active Directory Access
- DSProxy (DSProxy.dll) – Provides Directory Service Lookup for older Outlook clients
- Server Monitor Component – Monitoring server resources
- Mailbox Manager Component – Managing mailboxes
- Metabase update service – Replicating settings from Active Directory to the IIS metabase
- System Attendant Component – Verifies computer account configuration
DSProxy
DSProxy provides both proxy and referral services. Outlook clients running Outlook 2002 Service Release 1 and earlier versions use the DSProxy functionality because these clients were programmed to use Exchange Server as its directory service like in Exchange Server 4.0 to 5.5. DSProxy emulates a directory service, so that earlier clients can use the functionality. Exchange Server 2007 server forwards the requests to Active Directory.
- Emulate a MAPI address book service
- Proxy requests to an Active Directory server
DSProxy provides both proxy and referral services. Outlook clients running Outlook 2002 Service Release 1 and earlier versions use the DSProxy functionality because these clients were programmed to use Exchange Server as its directory service like in Exchange Server 4.0 to 5.5. DSProxy emulates a directory service, so that earlier clients can use the whole functionality. Exchange Server 2007 server forwards the requests to Active Directory.
Later versions of Outlook, beginning with Outlook 2000 with SR-2 and Outlook 2002/2003, are designed with the assumption that Exchange Server 2003/7 does not have its own directory service. After DSProxy has relayed one of these Outlook clients to a global catalog (GC) server, the client communicates directly with Active Directory.
DSAccess
Several Exchange 2007 services access information that is stored in Active Directory and write information to the Active Directory. If this communication occurred directly between each service and Active Directory, Exchange 2007 could overload a global catalog server with communication requests. DSAccess is the component which controls the interaction between Exchange requests and the Active Directory. DSAccess provides its own cache (DSAccess cache) for faster information retrieval.
DSACCESS is used by the following Exchange services:
- Microsoft Exchange Active Directory Topology (MSExchangeADTopology)
- Microsoft Exchange Information Store (MSExchangeIS)
- Microsoft Exchange System Attendant (MSExchangeSA)
- World Wide Web Publishing Service (W3SVC)
DSAccess discovers the Active Directory topology, detects domain controllers and Global Catalog servers, and maintains a list of valid directory servers that are suitable for use by Exchange components. In addition, DSAccess maintains a cache that is used to minimize the load on Active Directory by reducing the number of Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) requests that individual components send to Active Directory servers. The DSAccess Cache is configurable through several Registry Keys.
Changes in Exchange Server 2007
One of the biggest changes to DSAccess in Exchange Server 2007 is the Active Directory driver when compared to DSAccess. The Active Directory Driver does not access and store directory information in its cache. The Exchange component which is using DSAccess at the moment is responsible for implementing the cache when it is needed.
RUS – Recipient Update Service – not used in Exchange Server 2007
The Recipient Update Service (RUS) used by Exchange Server 2003 for the provisioning of new and existing Exchange objects like mail enabled users, mailbox users and contacts is an asynchronous task which stamps Exchange objects with e-mail addresses based on Exchange recipient policies. Exchange Server 2007 does not use the RUS. In Exchange 2007, recipients are fully provisioned when they are created in the Exchange Management Console (EMC) or in the Exchange Management Shell (EMS), so the asynchronous RUS service used in Exchange Server 2003 is gone. The RUS API (Application Programming Interface) used to calculate new Exchange objects still exists in Exchange 2007 and is now used directly by Exchange Management Shell cmdlets or the GUI to provision these objects..
DS2MB – Directory Service to Metabase
The function of DS2MB is to replicate configuration information from Active Directory to the local IIS metabase.
DS2MB is implemented as a process in DS2MB.dll and the primary function is to synchronize Exchange configuration settings in Active Directory with settings in the IIS metabase. The DS2MB is an unidirectional process which replicates information only from the Active Directory to the IIS metabase. You can view and edit the IIS metabase with the Metabase Explorer from the IIS 6 Resource Kit.
Microsoft Exchange MTA Stacks service (EMSMTA.exe) – not used in Exchange Server 2007
The Microsoft Exchange MTA Stacks service (MTA) in Exchange Server 2003 routes messages through X.400 and gateway connectors to non-Exchange messaging systems. In a mixed Exchange Server environment with servers running Exchange Server 5.5 in the local Exchange routing group, the MTA is also used to transfer messages between Exchange Server 2003 and Exchange Server 5.5. This occurs because Exchange Server 5.5 MTAs communicate with each other in the local site directly through RPCs. Exchange Server 2003 must rely on this communication method for backward compatibility.
Exchange Server 2007 does not use the MTA object and the X.400 connector (which must use the MTA) is gone in Exchange Server 2007. There are no longer any X.400 default proxy e-mail addresses in Exchange Server 2007.
Routing Engine (RESvc.dll) – not used in Exchange Server 2007
The Exchange Routing Engine service provides topology and routing information to servers running Exchange Server 2003. Exchange Server 2007 does not use the routing engine (RESVC.DLL) component. SMTP routing is handled by the Microsoft Exchange Transport engine (MSExchangeTransport).
IIS Admin service
The IIS Admin service (IIS Admin) manages the IIS Metabase and updates the registry for the following services:
- WWW service
- FTP service
- SMTP service (not required and supported in Exchange Server 2007)
- POP3 service
- IMAP4 service
- NNTP service
The IIS Admin service also provides access for other applications to the IIS configuration information, such as to the metabase update service, which is an internal component of the system attendant.
The registry key for the IIS Admin service is HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\IISAdmin.
Note:
Exchange Server 2007 does not depend on the IIS 6.0 SMTP service. Exchange Server 2007 uses its own SMTP stack implemented in the Microsoft Exchange Transport service.
Exchange Availability services
The availability service in Exchange Server 2007 is used to provide Fee/Busy information for Outlook 2007 clients, Outlook Offline Address Book generation (OAB) and Out of Office features, also for Outlook 2007 clients or Exchange Server 2007 Outlook Web Access (OWA). The Availability service is implemented in the Client Access Server role (CAS). The Availability service is the replacement for Free/Busy and OAB services in public folders used by Exchange Server 2003.

Figure 4: Exchange Web Services (EWS)
Conclusion
In this article I tried to give you helpful information about the Exchange Server 2007 services and how they work together. I hope you now understand better which services are new in Exchange Server 2007 and which services, used in Exchange Server 2003, are obsolete in Exchange Server 2007. There are more dependencies and services in Exchange Server 2007 but with the above-mentioned information you should have a good idea of how Exchange services work together.
Related Links
Exchange Internals – How the Exchange Core Components work together
Services installed by Exchange Server setup
Good bye RUS
Availability services FAQ

