
Cybercriminals can employ many methods to harm you. These malicious actors can use network security threats to exploit your network’s attack vectors or vulnerabilities. Networking threats come in different forms, but they all target a similar end goal: accessing your system to steal your data.
To protect yourself against cyberattacks, you must learn the possible threats to your network and how you can protect yourself against them. In this article, I’ll show you 8 different cyberattacks and some robust protection measures. Let’s dive right in!
8 Most Common Security Threats
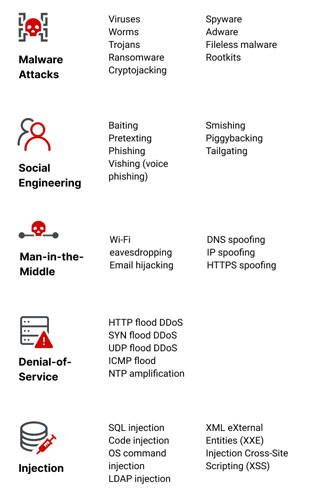
Over the last two decades, cyberattacks have become increasingly frequent, sophisticated, and difficult to defend against. Cybersecurity experts also believe network security risks will continue to grow more complex and aggressive. I’ll cover the 8 most common network security threats.
1. Malware Attacks
Malware is an all-encompassing term for malicious programs that cybercriminals use to damage a target network. In malware attacks, the cybercriminal utilizes malicious software to exploit security vulnerabilities and cause a data leak. Malware attack examples include:
Computer Viruses
A computer virus is malicious code that embeds itself in a genuine program, called a host file. The virus also takes advantage of the program to replicate itself. Viruses may remain dormant in a system until the user executes the host program. Then, the executed virus can corrupt, delete, or steal your data, compromise system security, and destroy your network structure. Viruses may also exploit your network to infect other systems.
Trojan Horses
Trojan attacks can give a cybercriminal unauthorized access to your network, steal sensitive data, or affect the overall system performance. In trojan horse attacks, cybercriminals hide malware behind a legitimate email or file to deceive you into running the program. Once you open the email or download the file, it immediately installs malware on your system.
Adware and Spyware
Adware is a program that monitors your browsing activity and uses your browsing data to constantly display unwanted advertisements. Developers may even include adware in their free programs to help recover development costs.
Spyware is a malicious program that invades your network privacy to spy on your valuable data and send it back to the malicious actor.
Computer Worms
A computer worm is self-replicating malware that takes advantage of a host network to infect many systems. Once a worm infects your system, it quickly explores your network for connected systems. Then, it makes copies of itself to infect those connected systems.
Rogue Security Software
Rogue software attacks start as pop-ups while you’re surfing a website. The pop-ups carry a message informing you that your system has viruses or an out-of-date security patch. The pop-up will prompt you to click a link to download paid software to erase the virus or update your security. However, downloading the software installs malware on your system.
2. Phishing
A phishing attack is social engineering used to manipulate you to divulge your passwords or other sensitive information. Phishing attacks commonly utilize phony emails. The email contents vary, but they generally prompt you into opening a malicious site. There, a malicious actor steals your data. Vishing is another common attack where the criminal tries to get confidential details over the phone.
Once the cybercriminal gains unauthorized access to your system, they may embed a rootkit in your network. A rootkit is a malware collection that hides deep within a computer’s operating system. Rootkits give cybercriminals backdoor access by evading standard network security measures. Cybercriminals can then control your network, disable anti-malware, or steal your data.
3. Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
In man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks, cybercriminals insert themselves in the middle of your private communications. This way, they can intercept data and communications between your device and another. They can then steal your data while it’s transmitted on the network. These cybercriminals may alter the information transmitted between both devices or steal sensitive private data.
Spoofing is also a common MITM attack where a cybercriminal disguises a display name, website, text message, email address, phone number, or website URL to convince a target they’re interacting with a known, trusted source.
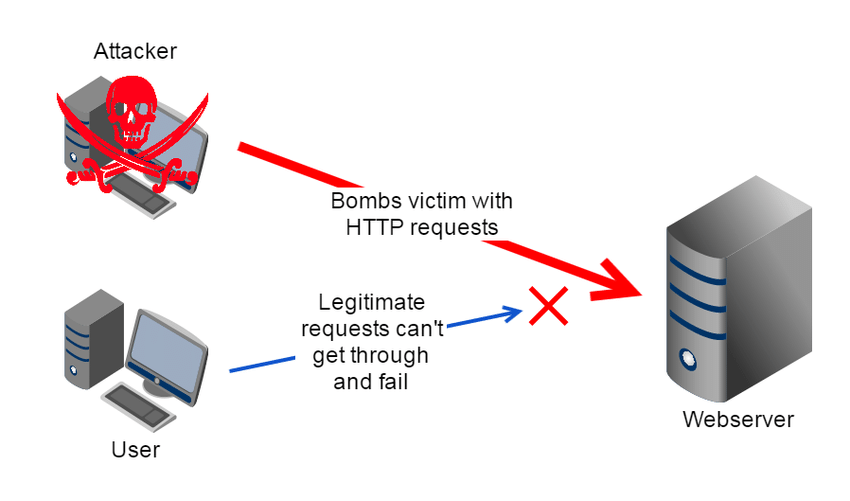
4. DoS and DDoS Attack
Denials of service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) are common networking attacks that target a website’s servers. These attacks work by flooding the server with data packets, causing the server to overload and crash. When this happens, legitimate website users can’t access its services.
The difference between DoS and DDoS attacks is that a DoS attack is carried out by one computer, while DDoS attacks are executed by several computers worldwide. Usually, the computers involved in a DDoS attack are part of a botnet that the cybercriminal creates by installing malware in a previous attack.
5. SQL Injection Attack
Many websites and web applications utilize SQL servers to store user data. Cybercriminals exploit a website’s server vulnerabilities to steal user information and other relevant data through SQL injection attacks. A malicious actor inputs a malicious SQL query in a web application’s input field during these attacks. The SQL database receives the malicious query, then executes the commands embedded within the query. As a result, this gives the cybercriminal control over the web application.
6. Privilege Escalation
Privilege escalation is a group of networking attacks that enable users to increase their permissions scope on a system. Cybercriminals commonly execute privilege escalation to increase their access to data after gaining unauthorized access to a network.
7. Insider Threats
Some security risks originate from people with authorized access to your security system. These are known as insider threats and are commonly perpetrated by disgruntled employees. They’re also hard to detect or prevent and are very costly to organizations.
8. Supply Chain Attacks
In supply chain attacks, cybercriminals gain access to your security systems by exploiting an authorized third party or outside supplier with access to your data and security systems. These attacks are hard to detect since the cybercriminal doesn’t exploit you directly. Rather, they take advantage of your supplier’s systems to gain access to your network.
Now that I’ve explained the 8 common networking attack types, I’ll address some common solutions to these attacks.
Protect Yourself Against Network Security Threats
You can employ several measures to protect yourself against various network security threats. These measures include:
- Patch management by acquiring and applying updates to existing software and applications.
- Cloud security tools and techniques to protect cloud-based data and applications.
- Endpoint security to protect network endpoints, such as computers and mobile devices, against security threats.
- IoT security, like monitoring and securing smart devices and their connected networks.
- Physical security to protect your physical infrastructure, including servers and data centers, against intrusion.
I also suggest using network security software to implement frontline defense against several common threats. Network security software continuously monitors your network traffic and alerts administrators if suspicious activity occurs. It helps to respond quickly and stop an attack before it causes too much damage. Let’s consider some of the best security software on the market!
Best Software for Network Security
After some research, I’ve identified the top 3 network security software options for maximum protection.
1. GFI KerioControl

KerioControl is a comprehensive network security risk management solution that provides intrusion detection and prevention, antivirus, bandwidth optimization, traffic monitoring, application, web content filtering, and firewall capabilities.
KerioControl is easy to deploy and features a simple online user interface. It’s the go-to network security solution for small and medium-sized businesses. KerioControl offers the following features:
- Out-of-the-box firewall configuration
- Efficient traffic monitoring and intrusion protection
- Easy, flexible deployment
2. Imperva

Imperva features a high-grade firewall, anti-DDoS solution, bandwidth optimization, and security monitoring and reporting capabilities to ensure your website is free from various network security threats. Additionally, Imperva provides:
- Simple architecture with fast deployment options
- Insightful attack vector analysis and reports on all websites
- Automatic updates and high-grade security for web applications
- Robust cloud security
3. Proofpoint

Proofpoint is an enterprise network security solution with on-premise and cloud deployment options. It provides an effective email protection solution by blocking unwanted or malicious emails. Proofpoint features include:
- Secure email routing using advanced firewalls
- Efficient email management to help users avoid spam or malicious emails
- Frequent data backup and recovery to ensure that users don’t lose valuable data
- Out-of-the-box regulatory and compliance policies to ensure organizations meet regulatory standards
Using network security software ensures you’re always one step ahead of unscrupulous cybercriminals!
Final Thoughts
Malware, social engineering, and denial of service are common network attack types that can occur at any time in any organization. If you don’t understand common network security risks, you can’t protect yourself against them.
Beyond understanding the risks, you must implement threat prevention techniques, including deploying network security solutions like KerioControl to ensure your data is safe from cyberattacks.
Do you have more questions about network security threats? Check out the FAQ and Resources sections below.
FAQ
What are the sources of a network threat?
Network threat sources include cybercriminals, hacktivists, hostile governments, government agencies, terrorists, industrial competitors, former employees, and even current employees. These sources usually have different motivations behind their attacks. For example, hostile governments may launch networking attacks to damage another nation’s systems, while cybercriminals may launch attacks for financial gain.
Can network threats go undetected?
Network threats often go undetected for prolonged periods before manifesting and causing phenomenal damage. Cybercriminals may also install malicious programs on a network to read and transmit data which they utilize for other attacks. Malicious programs don’t cause any overt harm and can go undetected, especially when no detection software exists.
How can you find hidden malware?
The most effective way to detect hidden malware is to download an efficient anti-malware software. Ensure the anti-malware solution comes complete with adware and spyware detection and that you regularly update it to get the latest functionalities. Additionally, run regularly scheduled scans on your system to detect any new malware.
How does malware spread?
Malware infects your system when you download infected software from untrusted sites or open malicious emails and attachments. Once on your system, the malware embeds itself on different programs. Then, it spreads using your network. So, when you send an email or file to a contact, it carries a copy of the malware. Malware also spreads when you transfer files via USB.
What is cyber security?
Cybersecurity is the act of protecting internet systems, including data, applications, and infrastructure, against cyber threats. These threats aim to exploit vulnerabilities in network security to steal sensitive data. Cybersecurity practices protect individuals and organizations that work on the internet against various networking attacks, ensuring their private data stays protected.
Resources
TechGenix: Newsletters
Subscribe to our newsletters for more quality content.
TechGenix: Article on Data Leaks
Learn how you can protect your organization against data leaks.
TechGenix: Article on Cybersecurity Trends
Read more about the latest trends in cybersecurity.
TechGenix: Article on Cybersecurity Strategy
Learn how to develop the most effective cybersecurity strategies for your business.
TechGenix: Article on Types of Malware
Explore malware attacks in detail to protect yourself better.




In 2013, the “Snowden Incident” broke the scandal that the United States used the so-called “Prism” project to monitor the leaders of allied countries on a large scale.