When Windows2000/XP is configured for TCP/IP “to Obtain an IP address automatically” via DHCP, it will first attempt to locate a DHCP-server (which can takes some time ). If no DHCP
server is found on the network, it will use the build-in “Automatic Client Configuration”
(sometimes referred to as APIPA ) to assign itself an IP-address in the address-range 169.254.x.x
with Subnet- mask 255.255.0.0.
On a large network with a predefined address range, this is often not required, because it will make
the trouble-shooting of networking problems more difficult when Windows2000 / XPtakes such an
“initiative” on its own. It is possible to de-activate this feature.
(The required changes in the registry are listed on the Microsoft Knowledge base articleQ244268):
You can deactivate the AutoIPgeneration for the complete computer using the Registry-key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
Add the following value to this key: “IPAutoconfigurationEnabled“, Value type: REG_DWORD
Value in hexadecimal: 0 (A value of 0 disables APIPA support on this computer) :
You can deactivate the AutoIPgeneration for just one or more network adapters:
You need to find a registry entry under:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\system\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters\Interfaces\<adapter>
The <adapter> is listed as an internal number .
If you have problems to identify the proper adapter, see the steps below.
Create a new DWORD-key “IPAutoconfigurationEnabled” with the value set to 0 :
When restarting now Windows2000/ XP and no DHCP-server is found on the network,
no IP-address will be assigned:
in a Command-prompt window, run : ipconfig
Windows 2000 IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection
| Connection-specific DNS SUffix . : IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . . Default Gateway | 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 |
the IP-address “0.0.0.0” is invalid, it indicates that your system has no IP-address
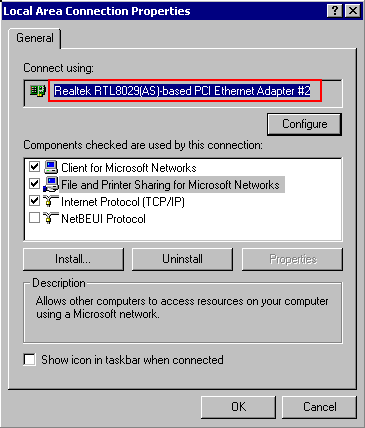 | How to identify the registry key for your network adapter ? Check in the Properties of your Network configuration the EXACT name for your Network card, as listed under: Connect using : ( select it by dragging and copy it to the clipboard) |
Search now the Registry for that “Adapter Description”, you need to find the “ClassGUID“,
a PCI-network card will be listed under
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\system\CurrentControlSet\Enum\PCI :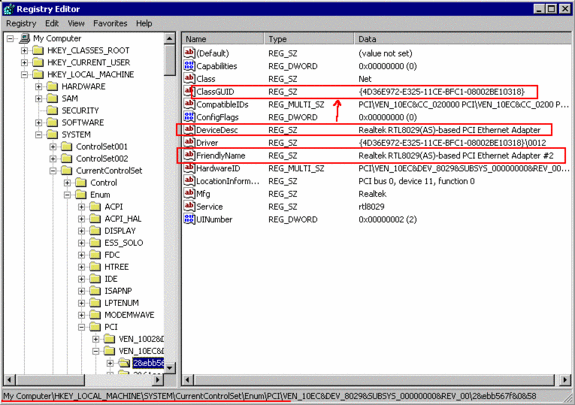
with the “ClassGUID”, search in
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\system\CurrentControlSet\Control\Class\ for this class”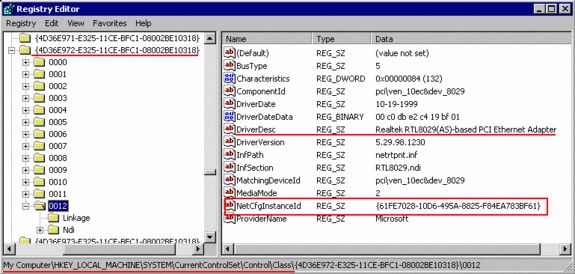
Check the sub-keys for the proper DriverDescription to match your network card.
and look for the Key “NetCfgInstanceID“, which is identical to your <adapter> number.
if you have multiple matches showing the same DriverDescription, check under the sub-key
“Linkage” for the “UpperBind” to be “TCPIP” (just “TCPIP” , not more ! ) :