As part of your network check, you need to verify your TCP/IP-configuration
( if you intend to use TCP/IP-protocol):
– Properties of “My Network Places” on your Desktop (via Right-Click), then
– for your network connection (“Local Area Connection“), right-click and select Properties :
The “Local Area Connection Properties” will show:
Connect using : <your network adapter>
Components checked are used by this connection :
– Client for Microsoft Networks
– File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks
– Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)
(when selecting/clicking on any of these components, the box “Description” will show a description)
– then click on “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” and select the button “Properties“: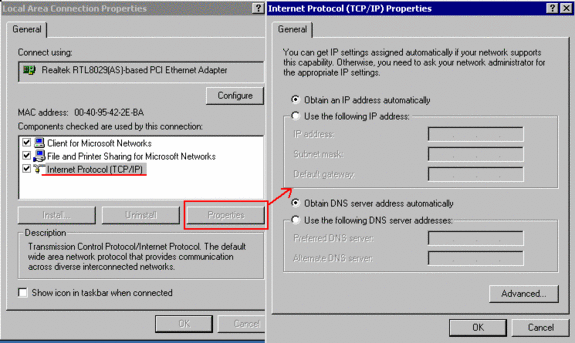
Windows 2000/XP has configured TCP/IP “to Obtain an IP address automatically” , i.e. via DHCP.
Lets verify the current TCP/IP configuration:

Unluckily, I could not find the equivalent of the Win95/98 utility “winipcfg“ included with
Windows 2000/Xp (there is a “wntipcfg” available as download from Microsoft) , so I use the same utility
as under NT4: “IPCONFIG”
– select from your Start-Menu: “Programs” / “Accessories” / “Command Prompt“,
– enter: IPCONFIG
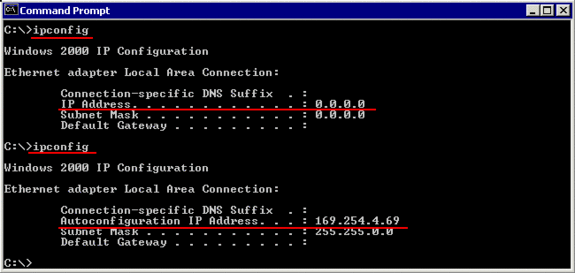
Sample Reply:
| Windowss 2000 IP Configuration Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection: | |
| Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : Autoconfiguration IP Address . . : Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . : Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . .: | 169.254.4.69 255.255.255.255.0 |
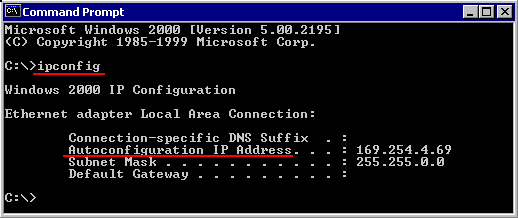
Note the info, that the IP-address has been generated by the “Autoconfiguration“, not via DHCP.
( IPCONFIG can also be used to request a new IP-address: to ReNew the IP-address )
 If you do not want Windows XP to use the Auto IP Configuration, you can configure a static IP-address to be used in case that no DHCP-server was found on the network. |
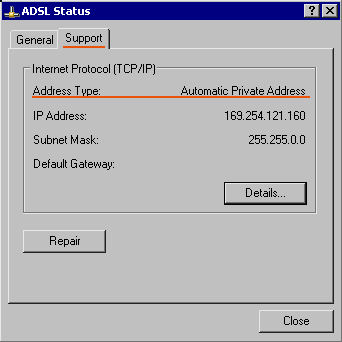 |  Windows XP allows to check the IP-address via “Network Connections” by displaying the “Status” of a connection ( right-click the connection , pop-up menu ) :  tab : Support |
| Note: when booting Windows2000 / XP , the start-up process will NOT wait for the DHCP / IP-Autoconfiguration process to be completed (as on Windows98, where this causes a boot-delay of several seconds). When making quickly the Login and using IPCONFIG, the IP-address may not yet be established, the system will then display as IP-address 0.0.0.0 : Example:
( you have the possibility to disable the Auto IP-address generation ). | ||||||||
 |  | If you do not like to use the Command-Prompt window, you can view this information also via the Control-Panel : “Administrative Tools” in the “Computer Management“:, section |
Look under “System Tools“/”System Information“/”Components” /”Network” / “Adapter“: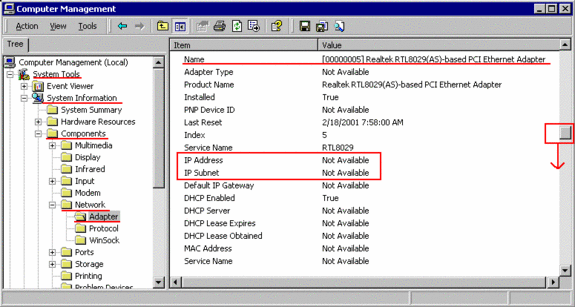
 |  | In Windows XP, “System Information” is not anymore included in “Computer Management” but a stand-alone utility, which is selected via the Windows Menu Programs / Accessories / System Tools |
Look under “Components” /”Network” / “Adapter“: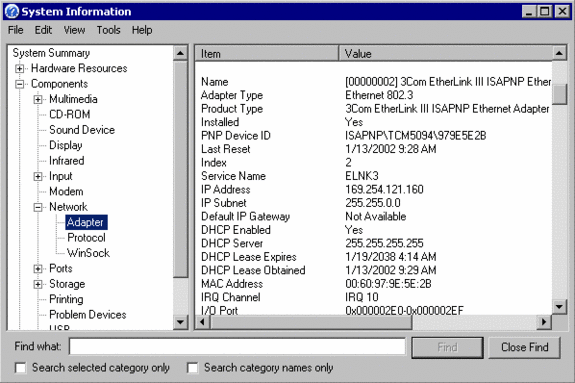
search in the right plane for your network adapter (example: the Realtec RTL8029) , it may be
defined multiple times in the list. If you find as IP-address: “Not Available“, continue to scroll down: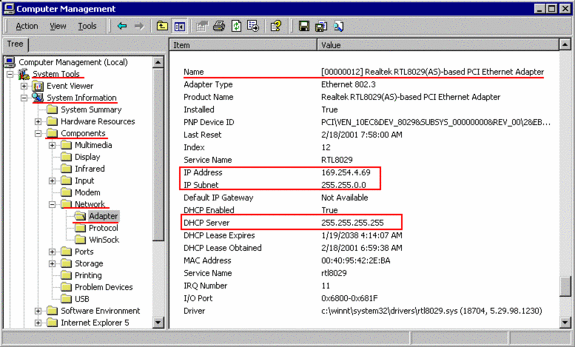
As Windows98, Windows2000/XP tries first to find a DHCP-server on the network.
If this fails, it then uses its own “AutoConfiguration” method to generate an IP-address. In such
cases, the “DHCP Server” in Computer Management (see above) is marked as 255.255.255.0.
( you have the possibility to Disable the Auto IP-address generation )
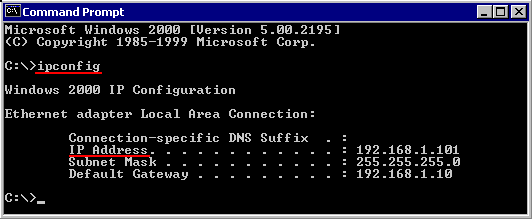
In case that a DHCP-server is found on the network and the DHCP-server assigns an IP-address,
then IPCONFIG shows a slightly different information:
Sample Reply:
| Windowss 2000 IP Configuration Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection: | |
| Connection-specific DNS Suffix . : IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .: Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . : Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . .: | 192.168.1.101 255.255.255.255.0 192.168.1.10 |
In “Computer Management“, it will list the IP-address of the DHCP-server, which assigned the
IP-address to this system: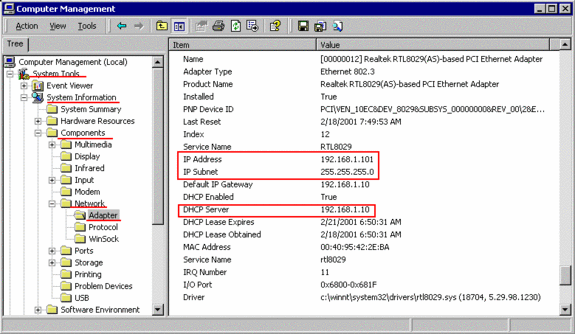
But a lot of networks work with a predefined range of IP-addresses (which also shortens the Boot-up time
of Win98 and Windows2000, since they do not have to wait anymore for the request to a DHCP-server to time-out):
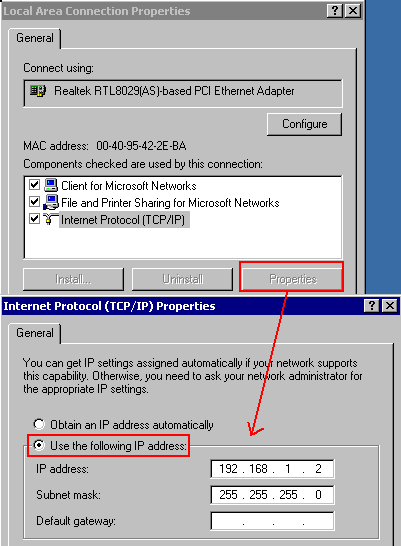 | My home-network uses the IP-range reserved for private networks: 192.168.x.y, so I am assigning manually the IP-address: 192.168.1.2 |
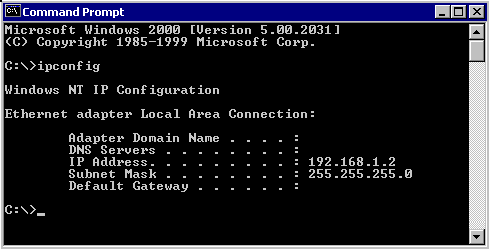
Nice new feature on Windows 2000 / XP : after changing the IP-address, it is NOT anymore
required to restart the system (like on Win95/98/Nt4), so I can run again “IPCONFIG“
to check the change:
Example:
| Windows 2000 IP Configuration Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection: | |
| Adapter Domain name . . . . . : DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . . . .: IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . : Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . . . . : Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . . . .: | 182.168.1.2 255.255.255.255.0 |
A last low-level check to verify, that the network is working, using the
TCP/IP diagnostic tool “PING” to test the connection to another system on the network:
Example :
C:\>ping 192.168.1.1
pinging 182.168.1.1 with 32 bytes of data :
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.1.1: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128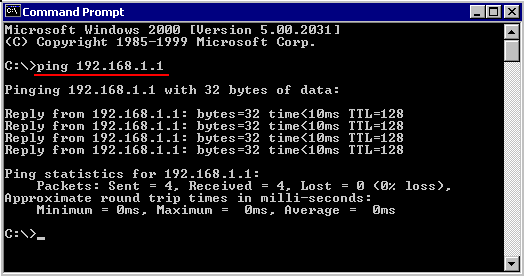
If PING does not get a reply, verify your TCP/IP settings and trouble-shoot your
network card and cables.