Whether or not you are aware of what it is, you have definitely heard of blockchain. Originally a concept developed to work with the cryptocurrency bitcoin, it has now evolved into a phenomenon everyone is intrigued by. But even when you know what blockchain is, there is still one big question: What role is there for blockchain in the enterprise?
To understand blockchain itself, we need to understand hash trees. Hash trees are data structures based on the encryption of data. They are essential in maintaining data integrity in a peer-to-peer network of computers during data transfer. Using hash functions hash strings were generated. Then, these randomly generated strings of a fixed length were decrypted at the destination to make sure that data transfer was complete and no false data was sent.
In 2008, a group of people (or an individual going by the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto) developed bitcoin using blockchain, which turned out to be a ground-breaking feat. Blockchain is a distributed and decentralized network of nodes. Every valid transaction is added to the blockchain ledger as a block and as this ledger is available to every node on the network, there is an absence of ambiguity.
How does blockchain work?
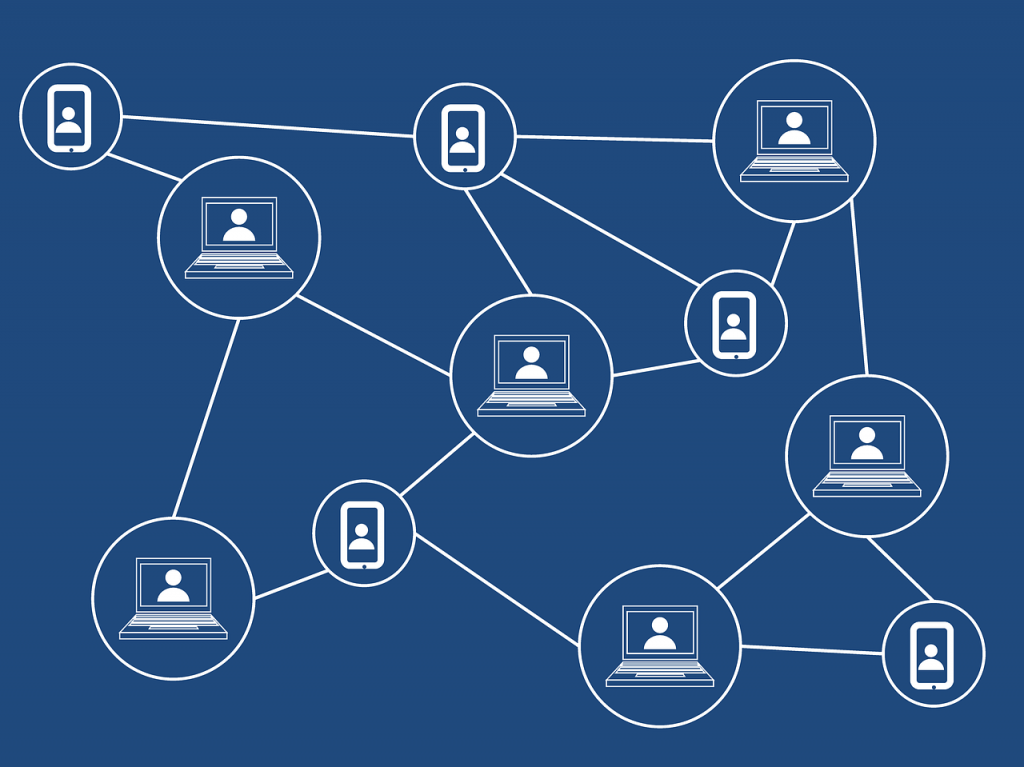
The blockchain is automatically reconciled every 10 minutes and the data is not stored at any one place — it is distributed across numerous computers spread across the world. There is no master or centralized version of data that can be hacked into or forged, which provides incredible security and transparency. Every transaction is verified by all the nodes on the blockchain network. If the transaction is considered valid, the transaction is saved in a block. A block in blockchain refers to a group of transactions. These transactions get stored in the order they are performed in. Blockchain ledgers are immutable and hence it’s not possible to forge any transaction.
The Google Docs analogy
William Mougayar, a blockchain specialist, explains blockchain using the following analogy:
“With Google Docs (or Google Sheets), both parties have access to the same document at the same time, and the single version of that document is always visible to both of them. It is like a shared ledger, but it is a shared document. The distributed part comes into play when sharing involves a number of people.”
Mougayar says that the way we share our data today does not allow more than one user to make changes to it at the same time. The data is completely locked for other users when one user is manipulating the data. This is done to maintain integrity of the data. Banks use the same technique to deal with money in people’s account. Hence, the balance is decreased before the transaction is even complete. But, with blockchain’s distributed ledgers, like Google Docs, the transactions can be easily traced back and multiple people working on the same data won’t be an issue.
Enhanced security
Today, we use the username/password system to protect our online assets, but that is imperfect, to say the least. Blockchain uses the concept of encryption. Every user has a unique pair of keys called a public key and a private key. The public key is a string of characters that help identify users on the blockchain network whereas the private key is the secret key that in combination with the public key helps make a unique signature of every user. Using these signatures, the transactions are validated and traced. This makes the data you keep in the blockchain networks incorruptible. Since the data is not centralized, every node has access to the data which provides transparency.
The blockchain hype
But what blockchain in the enterprise? Blockchain has gained significant momentum in recent years and its success is attracting enterprises that want to use this technology. The blockchain concept can be applied to various use cases from financial services to retail to health care and beyond. Various big companies are trying their hand in blockchain. Many of the Fortune 500 companies are working on proof of concepts and pilots based on blockchain technology for its applications to improve security and make business operations more efficient. Airbnb, Daimler, Rakuten along with various others have acquired several blockchain-related startups. JetBlue, Verizon, and others are making strategic investments in the technology.
Blockchain consortia
Recently, many companies have joined forces to form what is being referred to as consortia. Most of these consortia are in the financial sector. However, there are a number of consortia developing proof of concepts in other sectors. Consortia offer a lower risk to the individual enterprises. With good funding by the key enterprises, a consortium can make definitive progress in the implementation of blockchain technology. Blockchain is essentially considered to be a foundation for an efficient cross business platform and various competitors are working together to develop models and set standards for this technology. R3, one of the largest consortia, consists of more than 100 banks, regulators and trade association firms. R3’s Corda is a blockchain platform that is still being tested. Other consortia include Hyperledger, Mobility Open Blockchain Initiative (MOBI), and Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA).
Blockchain use cases
And now to the main theme of this story: A look at some real-world uses of blockchain in the enterprise and the various applications of blockchain that can help revolutionize industries. Blockchain-based projects have raised exponential capital in recent years and with time new use cases, spanning private and public sector services alike, are coming into the picture. Here are some of the most compelling blockchain use cases.
1) Supply chain management
There is a major issue firms are dealing with when it comes to supply-chain management. There is a lack of transparency between suppliers. Hence, increasing accountability for all the middlemen is a priority. With blockchain’s distributed ledgers, this issue can be resolved. Blockchain allows multiple people to access the same database which will increase transparency in the supply chains. Blockchain ledgers are immutable and all the valid transactions are appended with a timestamp which can help in auditing and stop theft and counterfeits. This use case can improve regulatory compliance, reduce paperwork and help cut cost significantly. IBM has recently released its blockchain based product called Food Trust that helps implement this use case. Prior to this, IBM had been in partnership with Walmart to help track the journey of food staple from supplier to the shelf. Blockchain can also help consumers in finding out if the product really is what it claims to be. This ledger system can also help pharmaceutical companies keep a track of medicines.
2) Protecting digital identity

Identity theft has become very common today and improvements in digital security haven’t been able to provide a definitive solution to the ever-growing need for Internet security. With blockchain’s immutable ledgers, users can store their personal data securely. Due to its decentralized network, data on blockchain is not vulnerable to hacking. A sovereign user ID can help users access their data without any hassle. Civic’s Secure Identity Platform provides users with a multifactor biometric authentication void of usernames and passwords. Verifiable ID is created by making users go through various identity checks. This ID can be used by governments or banks to review users’ encrypted information. Moreover, this ID can collect user’s social media credential and medical records and store all that information securely on blockchain. Not only can this digital ID help users perform online transactions securely and efficiently, but this can also help in stopping companies from monetizing on people’s data.
3) Smarter predictive analysis
With all the transaction data stored on the blockchain ledgers, these ledgers can help excavate huge amounts of data and insights. Blockchain-based artificial intelligence can help make accurate forecasts. Endor, a blockchain-based AI, uses natural language processing to answer questions in real time. With its help, businesses can make use of blockchain data in their projects, privately.
4) Health care
Currently, people’s medical history and records are not properly documented. The data sits on legacy silos, which leads to restrictions in sharing of data instantly. With the help of blockchain, the medical history of an individual can be stored securely on the distributed ledgers. This data will be easy to access when the need arises. Different stakeholders can have conditional access to the distributed ledger. Blockchain will help keep an audit trail on individual’s medical history through time stamp. Users will also be able to monetize on their medical data for research purposes.
Medicalchain, a blockchain based startup that’s yet to pilot, uses the technology to safely record individual’s health records. This information can then be provided to doctors, pharmacists, and health insurers. All the transactions can be recorded to give users control over their data.
5) Energy

Blockchain provides a compelling solution for the energy market. By recording people’s utility in a ledger, the data can help people deal with energy like any other commodity. Currently, large corporations sell energy at fixed prices, but with the implementation of this use case, the energy market will be forced to follow supply and demand in a particular region. The intelligent metering of electricity will help users to be consumers as well as producers which will reduce costs significantly. Australian startup, Power Ledger makes use of blockchain ledger to track energy usage and help users easily trade energy without having to rely on a centralized grid. It aims at providing more resilience to the energy market.
6) Land title registration
Frauds are common in property registration. However, using blockchain ledgers, the record keeping will be efficient and the chances of fraud will be reduced significantly. Blockchain’s solution will also help reduce labor and lessen paperwork. This use case has seen some serious traction in recent years where countries after countries are joining in and tying up with blockchain based startups to implement it. Recently, China, India, Sweden, Kenya, and several other countries have shown interest in this technology.
The future of blockchain in the enterprise
Blockchain’s advantageous tech has the potential to transform the Internet as we know it. There are challenges because of tech’s immaturity, but the increasing investments and R&D promise a bright future. It’s not an easy road, as many companies can be reluctant in implementing blockchain. But blockchain can help with that by providing conditional information based on what needs to be shared. With more enterprises trying to join consortia to work on blockchain proof of concepts and pilots, it’s won’t be long before large-scale projects are introduced. Blockchain has emerged as a disruptive technology and it’ll be an exciting journey for this tech as it takes the world by storm.
Featured image: Shutterstock



