Cloud computing is overtaking the business world and replacing standard storage and drives. As companies continue to shift to the cloud, it’s essential to protect their digital assets. That’s where cloud network security comes in! If you’re proficient in cloud network security, your company can run workloads in any type of cloud. These types include public, private, and even hybrid clouds.
In this article, I’ll go through what cloud network security is and why it’s important for your company. I’ll also introduce you to the different aspects of cloud security. You can use this as a jump-off point as you begin exploring deeper into the subject.
What Is Cloud Network Security?
Cloud network security is a branch of cybersecurity that focuses on ensuring the security of cloud computing systems. You can generate, process, and store many business and personal data, like financial and credit card data using cloud network security systems.
Cloud network security also includes all aspects of securing every component in the cloud, from virtual machines, through configurations, to applications and data. The purpose behind cloud security is to shift the risk of data loss, unauthorized access, and service interruption. It also helps you avoid performance degradation, data breach, and anything compromising your system in the cloud.
Cloud security enhances your company’s knowledge in protecting cloud-based digital assets. When you apply this knowledge, you also improve your company’s ability to comply with data privacy/protection laws and regulations.
Now that you know what cloud network security is, I’ll guide you through 5 reasons why cloud security is important for your company.
Why Is Cloud Network Security Important?
Adding cloud security as a business priority might seem unnecessary and impractical, but it’s not. Check out 5 reasons why cloud network security is important below:
1. Reduces Business Risk
As you migrate workloads to the cloud, you increase your attack surface. Why? Before, you only had to worry about potential threats and vulnerabilities in your on-premise IT infrastructure, which impacted business operations. Now, you also have to contend with similar concerns in your private, public, and hybrid clouds. When you adopt cloud security, you reduce risks in those areas.
2. Protects Data
Cloud environments generate, process, and store huge amounts of data every day. In fact, predictions say that by 2025, 100 zettabytes, or 50% of the world’s data at that time (up from 15% in 2015), will be stored in the cloud. Some of that will be sensitive data, e.g., personal data, financial data, trade secrets, credit card data, etc. Your company also needs cloud security to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of that data.
3. Increases Reliability and Availability
A significant part of your business processes run in the cloud, so you need to constantly keep the cloud services driving those processes reliable and available. Cloud security also helps you prevent processes from being deliberately or accidentally corrupted or disrupted.
4. Ensures Regulatory Compliance
Data protection/privacy laws and regulations cover certain types of data stored in the cloud. These laws could be the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), among others. When you implement cloud security best practices, you increase your chances of staying compliant with these mandates.
5. Reduces Costs
The price of a single data breach costs you much more than cloud security initiatives. Data breaches are more likely to happen in the absence of cloud security. In the 2021 Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average total cost was already estimated to be at $4.24M, with the average cost of a mega-breach (50-65 million records) already at $401M. That means you’ll have to spend on potential lawsuits, legal and regulatory fines/penalties, data breach notifications, and other related costs. You’ll also suffer a loss of opportunity and a severely damaged reputation.
Indeed, you shouldn’t take cloud security’s importance lightly. That said, I should say the road to a secure cloud environment has bumps and potholes. In the next section, I’ll tackle the top 4 challenges you’ll likely face along the way.
Top 4 Challenges to Cloud Security
When launching your cloud security initiatives, you’ll face some major challenges at times. Here are the top 4 challenges you may encounter:
1. Shadow IT
Cloud services (especially Software as a Service applications) are both easily accessible and easy to use even for regular end-users. This is why many employees subscribe to these services without informing their IT department. Security-conscious personnel doesn’t manage or conduct the processes and transactions that shadow IT practitioners conduct with these services. That means these processes will be grossly unprotected. Indeed, how can you protect something you’re completely unaware of?
2. Collateral Damage of DDoS Attacks
The moment you migrate your workloads to the cloud, you expose it to threats you don’t normally encounter in traditional IT environments. One of these threats is Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. DDoS attacks are cyberattacks directed at IT infrastructure with the intent to disrupt services. High traffic volumes mainly distinguish this kind of attack.
Companies that aren’t the object of DDoS attacks may still suffer collateral damage along, especially if the object of the attack is a public cloud. This is likely to happen because several tenants share services and resources in a public cloud.
3. Cloud Misconfigurations
One cloud computing benefit is that it greatly simplifies many executive tasks. Even a junior executive can easily spin up a server or set up a multi-terabyte storage. Unfortunately, that benefit also makes it highly susceptible to human error. A simple accidental misconfiguration can easily expose sensitive data or a server instance to the general public and cause a data breach.
4. Vulnerabilities at Scale
A major advantage of cloud infrastructure is its exceptional scalability. As a cloud admin, you can easily deploy thousands of servers and applications in a very short period. You can do this through leveraging auto-scaling, Infrastructure as Code (IaC), containers, and DevOps practices. If an image has vulnerabilities though, all those servers/applications generated from it will inherit those vulnerabilities. This means you could end up generating thousands of server instances or containers exposed to a range of threats.
These are just some of the many challenges present in cloud environments. While they might seem pretty daunting, you can address them in some ways. In the next section, I’ll tackle some of the solutions out there, including a few to help you address these challenges.
6 Types of Cloud Security Solutions
Cloud environments are often very complex. They consist of many components, including virtual machines, applications, and application programming interfaces (APIs). These components also include user accounts, data, and many others. Meanwhile, these cloud environments face an array of threats and vulnerabilities. You can only benefit from cloud systems if you prevent these threats and take action from the beginning.
Consequently, cloud infrastructure security is a very complex field. You need to employ a variety of security solutions and controls for your company. Each of the solutions targets a specific set of threats and vulnerabilities. Here are 6 types of cloud security solutions:
1. Behavioral Analytics-Enabled Solutions
Behavioral analytics is usually employed on network traffic, files, and user sessions to identify malicious behavior. Some analytics solutions compare artificial intelligence (AI) and Big Data with well-understood patterns and trends to analyze anomalous behavior. This makes behavioral DDoS protection solutions more effective than their traditional counterparts. That’s because they can distinguish legitimate traffic from malicious ones when a DDoS attack is underway. DDoS solutions can also allow legitimate traffic to pass through. When you use behavioral analytics tools, you’ll directly identify the presence of any odd or high risk in your system.
2. Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP solutions help prevent sensitive information like your personal information, credit card data, and financial information from falling into the wrong hands. These solutions detect the location of your information. DLP solutions then ensure that no one can download/upload, copy, transfer, etc., your information without proper authorization. Through this functionality, you can restrict unauthorized data flow to applications to use DLP against shadow IT practices.
3. Privileged Access Management (PAM)
The principle of least privilege restricts users to minimum access levels based on the requirements they need to accomplish their job functions. Grounded on the principle, PAM systems help mitigate the risk of cloud misconfigurations. PAM systems can control, monitor, and secure both human and non-human privileged accounts and their activities. That way, you can also avoid accidental and intentional cloud misconfigurations.
4. Vulnerability Scanners
To state the semi-obvious–vulnerability scanners scan systems for vulnerabilities. When you apply vulnerability scanning to a cloud environment, it can be more effective if you direct the scanning to the images themselves. That way, you can catch vulnerabilities before the images in question generate any virtual machine or container.
5. Antivirus and Antimalware Tools
Like regular IT systems, malware can also infect cloud-based systems. If that happens, the system, and even the hosting cloud environment, can suffer performance issues, data loss, or (in the case of ransomware) complete downtime. Antivirus/antimalware tools provide threat detection and prevention capabilities to help mitigate these threats. Intrusion prevention and detection systems provide the same protections.

6. Access Control
Access controls ensure people and applications requesting access to your cloud environments are authorized . You can use security controls like password-based authentication, public key infrastructure (PKI), biometrics, and multi-factor authentication to enforce access control policies.
The proliferation of security point solutions, like those mentioned earlier, combined with the lack of talent in the cloud security space, has given rise to products and services that seek to consolidate security tools and/or simplify security in cloud environments.
Some examples of these products and services include Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs), Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) systems, and Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) solutions. Regardless of which security solution you use, you have to remember that an all-in-one solution doesn’t exist. Even if it did, you can’t build a robust security infrastructure using a one-size-fits-all approach.
When implementing cloud network security, you have to consider some key things. I’ll now discuss 7 of them
7 Things to Consider When Implementing Cloud Network Security
While most of the security concepts are used in traditional on-premises IT infrastructure, cloud network security has certain intricacies you should be aware of. Knowing what they are can help you become more effective in implementing cloud network security.
1. Understand Your CSP’s Shared Responsibility Model
Implementing cloud network security requires you to follow what’s known as a shared responsibility security model. A shared responsibility model is a framework between you and your cloud service provider (CSP).
This model clarifies the duties you’re responsible for and which fall under your CSP’s responsibility. Here, you’ll need to understand your shared responsibility and ensure you’re familiar with what your CSP has published.
The shared security model can vary depending on the cloud service type (IaaS, PaaS, or SaaS). Here’s a simplified illustration of what a shared responsibility model may look like for each service type.
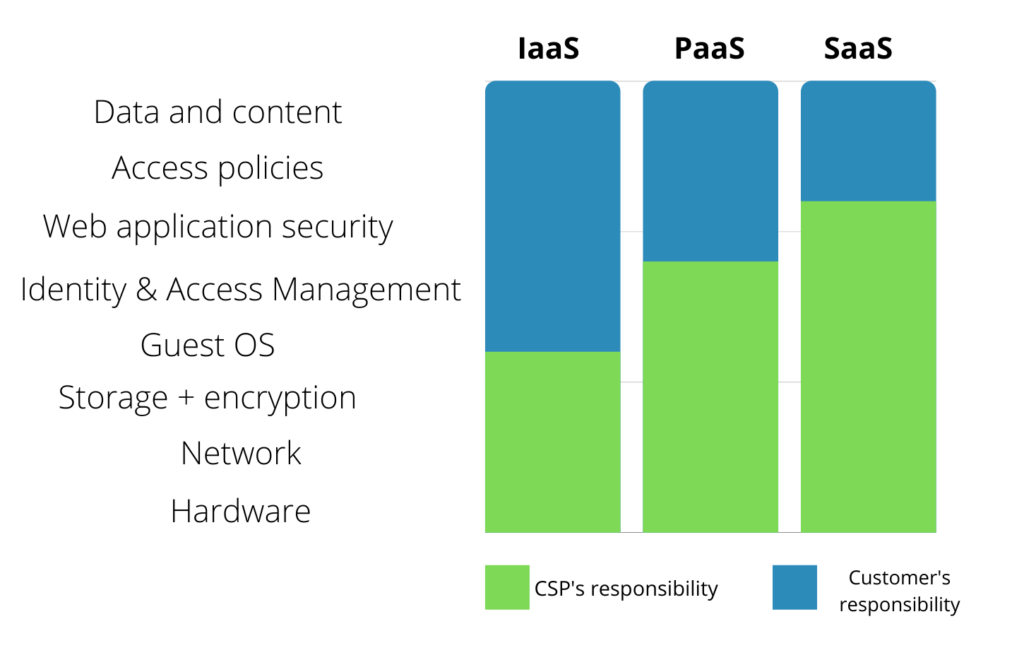
Every CSP also has its own version of this shared responsibility security model. So, you’ll want to review the model your CSP has published and discover the tasks you’re responsible for.
2. Maintain a Strong Security Password Policy
Password policies govern how users should craft their passwords. For example, they control the number and kind of characters you should use. Password policies also control how long you should use passwords before changing them.
Strong passwords can help to prevent dictionary-type attacks or brute force attacks. Here’s what you’ll need to create a typical strong password:
- Is long (e.g., at least 10 characters)
- Consists of both letters and numbers
- Consists of both uppercase and lowercase characters
- Includes special characters
- Change it on a regularly basis (e.g. every 90 days)
For your password policy to work, you need to apply mechanisms to automatically enforce it. For example, choose applications that readily support and enforce strong password policies. Don’t just rely on the user for enforcement.

3. Leverage a Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB)
Speaking of policies, one way to enforce them is to leverage a CASB. A CASB is a security solution that sits between a cloud customer and a CSP. It acts as a gatekeeper that allows certain activities to take place. CASB allows activities only if they adhere to the companies’ security policies. CASBs can also enforce a wide range of policies. For example, authentication (that includes passwords), authorization, encryption, logging, malware detection, and many others.
A CASB can be very handy since it greatly simplifies policy enforcement as well. That’s because it consolidates practically every single security policy you need for cloud network security. It can also be a godsend for cybersecurity teams responsible for dealing with several other aspects.
In choosing a CASB, you should ensure it integrates well with your existing security solutions. Your CASB should also support different types of services, e.g., SaaS and IaaS, if you’re following a multi-cloud strategy. This will help you maximize the potential of your cloud network security investments.
4. Use Software-Defined Access
Software-defined access isn’t just a security solution. It’s a solution designed to address network deployment, operations, and security challenges. Software-defined access also addresses challenges associated with managing both wireless and wired networks. To do this, it consolidates command-line interfaces, automation, monitoring, management, etc., into a single solution. This solution leverages policy-based automation.
Software-defined access is built for companies that directly manage the underlying infrastructure of a cloud environment. For example, you can benefit from software-defined access if you’re a CSP or a company managing your own on-premises private cloud.
5. Apply Network Segmentation
Network segmentation is network-level security in cloud computing. It allows you to divide a network into subnetworks or network segments. This can be useful in cloud environments where multiple companies, users, applications, or server instances share the same network.
Segmentation ensures that, should one segment be compromised, the other segments will remain safe. CSPs also provide built-in features allowing you to apply network segmentation in your own cloud environments. For example, in AWS, you can achieve segmentation through what are known as Security Groups. In Azure, they have what you call Network Security Groups (NSGs).
Before you apply network segmentation, visualize the layout of your network first. You also should understand your network’s current state first. That includes the users connecting to it and the components composing it. Your network’s current state also includes how those components interact with one another among other things. You need to gain a clear understanding of your current network before you can apply network segmentation correctly.
6. Use Encryption
Encryption renders data unreadable to those who don’t have the right decryption key. That’s why it’s an effective way of preserving data confidentiality in the cloud. You need encryption most in 2 situations. The first is when your data is at rest in your storage service. The second is when your data is in transit across the network.

You can also apply data-at-rest encryption in 2 ways. One is leveraging the built-in encryption services of your CSP. For example, AWS S3 has something called Server-Side Encryption. The other way is to use something like PGP.
On the other hand, you can also use secure file transfer protocols like HTTPS, FTPS, and SFTP to apply data-in-transit encryption. Protocols like HTTPS and FTPS rely on SSL/TLS, the same technology that secure websites use. This allows you to protect your data while transmitting it across the network against unauthorized users.
7. Establish an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan is your ‘plan B’ if a threat bypasses your defenses. No matter how seemingly tight your cybersecurity defenses are, the chances of a threat somehow slipping through are always possible. An incident response plan will also allow you to prepare for that eventuality.
This may also entail establishing your own in-house incident response team or hiring a third party. Cloud network security incident responders can help contain and minimize the impact of an attack on your infrastructure in case your defenses fail to hold.
Final Words
When moving to the cloud, you’ll need to implement good practices from day one. In order to do that, you’ll have to thoroughly understand the definition of cloud network security and why it’s important. You also have to understand the challenges you may face, the different types of solutions, and the best practices to consider when you implement cloud security.
Cloud environments, their various components, threats and vulnerabilities, and associated risks are a highly complex mix of concepts. That’s why it would be impossible to reply to the question “what is cloud network security?” with a single answer. I hope this article has provided sufficient information to help you on your quest to gain a deeper understanding of the subject.
Have more questions about cloud network security? Check out the FAQ and Resources sections below.
FAQ
What is a hybrid cloud?
A hybrid cloud is a combination of an on-premises private and public cloud. Integrating those 2 types is essential to building a hybrid cloud. The purpose of hybrid clouds is to enable your company to leverage the scalability and global reach of public clouds. They also aim to have the level of control that private clouds provide.
What is public key infrastructure (PKI)?
PKI is an infrastructure whose main functions include processing and managing digital certificates and their associated keys. In order to establish PKI, you need one or more certificate authorities (CAs) and policies that govern the PKI. You’ll also need digital certificates and applications that use digital certificates. PKIs serve to secure B2B as well as user-server transactions.
What are the best intrusion prevention and detection systems today?
Here’s a list of the best intrusion prevention and detection systems in 2022. This list takes into account various considerations like ease of configuration and use, reporting/logging capabilities, and cost. You’ll also find this list useful if you’re looking for a solution that prevents and detects inbound threats.
How to prevent a cloud data breach?
A cloud data breach is basically an unauthorized exposure of data (usually personal information) stored in the cloud. Legal and regulatory mandates cover certain types of data. That’s why you need to prevent breaches to avoid punishing fines and penalties. You can also employ a defense-in-depth strategy to prevent a data breach. This strategy includes applying encryption and leveraging the built-in security capabilities of your CSP. It also includes monitoring/logging network activities among other things.
What cloud network security red flags demand attention?
Cloud security red flags are security-related events or conditions in your cloud environment. These red flags serve as warnings. Failure to heed these warnings can lead to costly outcomes in the future. Some of these red flags also include multi-tenant crossovers, lack of standards, and the inadequacy of controls for data access.
Resources
TechGenix: Cloud-Native Security Guide
Discover 5 key areas of cloud-native security that will matter in the upcoming year here.
TechGenix: Cloud Computing Trends Article
Check out the top 6 latest trends in cloud computing in 2022 here.
TechGenix: Defining Moments for Cloud Computing Article
Look back at the defining moments in the world of cloud computing in 2021 in this article.
TechGenix: Guide on Cutting Cloud Costs in Half
Learn how to cut cloud costs in half in 4 ways here.
TechGenix: DoS vs DDoS Article
Understand the key differences between DoS and DDoS attacks here.