Given the extent to which IT has penetrated the business landscape, it is simply not acceptable for business managers to not know the basics of IT any more. And there’s especially no excuse after they read our guide to some IT basics that are key to good performance, control, and success.
Definition of business cases
In many instances, IT is left to define the business cases without adequate inputs from business managers. This should not be the case. It is critical for business managers to have a significant say in defining business cases for projects.
The starting point is to describe the exact business problem that is sought to be solved with the aid of technology. For instance, the business case may be that customer records in a database without a Social Security number need to be identified by a program. The purpose being that these customers are considered non-compliant and the company needs to get back to them to get Social Security numbers populated.
Business managers should be heavily involved in defining such business cases so that IT can focus on coming up with a technology solution to the problem.
Working with IT vendors

It is essential to understand how to contract with IT vendors. Some of the aspects surrounding this are the liabilities for all parties under the contract, how service levels are going to be defined, how service levels are going to be monitored, and what would happen when service level agreements are broken.
Other aspects include those related to how the vendor is going to maintain data and application security. For most of these aspects, business and in-house IT departments will be expected to work together. However, business managers should have adequate knowledge of these areas kind of like the creators of “24,” “The Walking Dead,” “The Wire,” and so on know how to create amazing programming since that is exactly what they did, but this is another topic.
Contributions of IT to an organization
It is often the case that IT is seen by business as an unresponsive department that does not work in sync with the organization’s needs. (HR gets this same rap and in some cases there is a point there to make.) However, such a perception may be unfair without having a comprehensive understanding of all the responsibilities that the IT department shoulders.
There are a number of activities that IT is responsible for, starting from development and maintenance of applications to tracking system assets. There are several more — keeping networks and applications up, managing ID assignments for IT systems for employees, having data protected adequately against breaches and viruses, among others.
IT basics related to information security
Information security is not just one of the IT basics. It is one aspect that business managers must also take responsibility for. Not only is this area intuitively simple to understand, it is also at the business manager level that problems related to this aspect can be addressed adequately. This means spreading awareness of the importance of avoiding ID sharing, appropriate usage of the web, and email related policies.
Aspects related to energy conservation
Just like information security, energy conservation is another of the IT basics that is very much in the realm of business managers to be on top of. Encouraging employees to maintain their device in sleep mode when not working and educating them on the importance of energy conservation are some activities that business managers can carry out.
While there would still be involvement of IT needed if some automated tools are to be developed, business managers can definitely take the lead in this area. Other aspects include the need to lock device screen when users are away and to switch off monitor as an alternative in such cases.
Developing reports
Most of the applications give you end-user reporting tools that help you develop your own basic reports. In the case of Microsoft Excel, the support is already there with pivot tables and the like. Of course, business managers would not be in a position to develop complex reports and if your business manager is Kelso from “That 70s Show,” Skids or Mudflap from “Transformers II,” or Charlie Harper from “Two and a Half Men,” then you are in trouble and you should expect no such report! That’s business basics, not IT basics.
But they should be in a position to develop simple reports themselves. Even applications like Crystal Reports provide a lot of features to end users to develop basic reports. Some of the usage can be complex like pivot tables in the case of Excel. But with a little bit of practice, it becomes eminently possible to develop reports by yourself unless your name appears right above — any report is beyond their capability.
Processes like SDLC and process standards
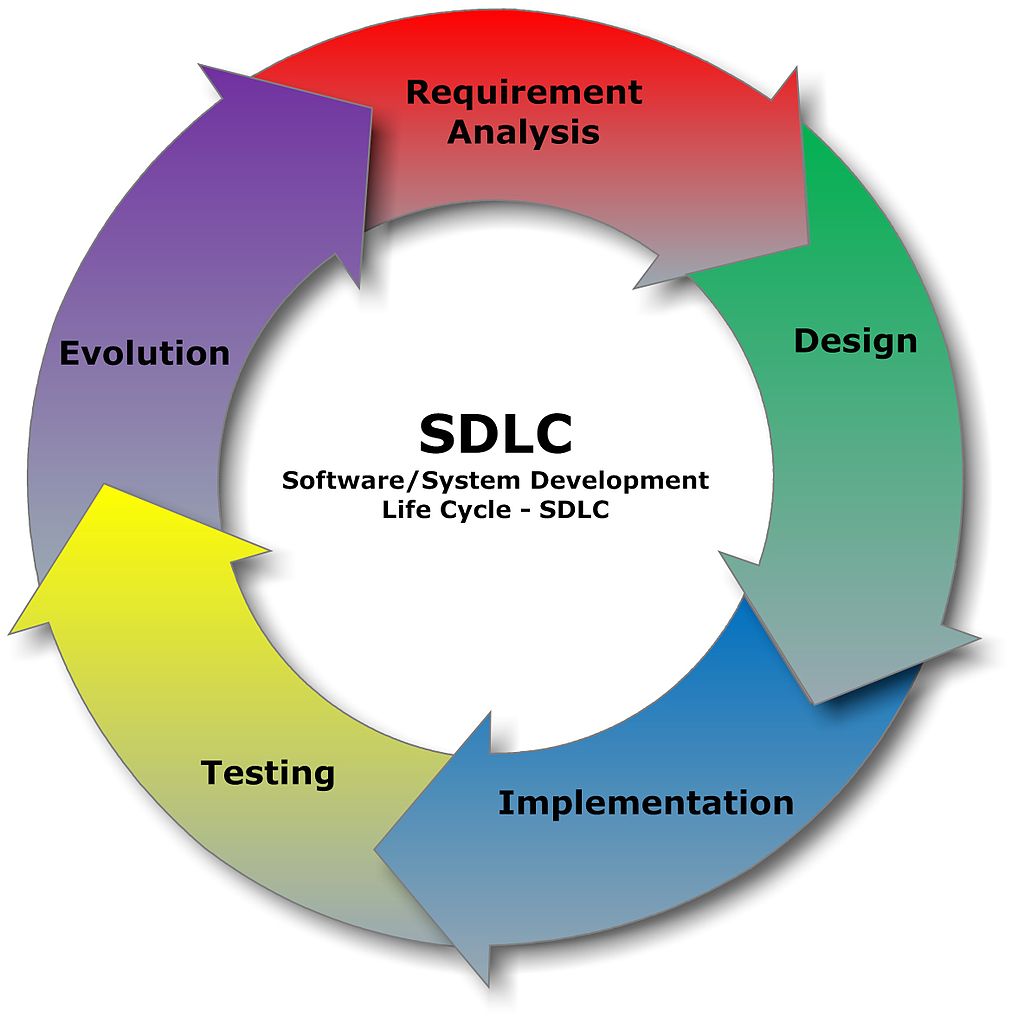
There are certain aspects of IT that business managers definitely ought to know, for instance, the SDLC, or the Software Development Life Cycle. Business managers must be aware of how this process is organized at a high level, i.e. analyze, design, develop, test. This is the process that describes the software development life cycle. Suitable knowledge of the IT process is needed if business managers need to effectively function during meetings and the like.
Business managers must also have concrete basic understanding of the standards generally followed by the IT department, such as CMM and ISO. While a deep understanding is not required, appropriate fundamental knowledge is required. This knowledge includes an understanding of the standard and how it is applicable to software.
In the case of CMM and ISO, it includes the knowledge of the responsibilities that one has once an organization has certified itself under CMM or ISO. Generally, it means that specific processes need to be followed for every step in the software development process.
Basics of software quality
Business managers should also have a fundamental knowledge of software quality. This means that business managers should have a solid grasp of the parameters used to measure software quality.
Some of the parameters that need to be understood include schedule deviation, effort deviation, defect count, defects in a phase, defect types, review defects, and review effectiveness metrics. A fundamental understanding of the associated parameters is critical if a business manager is to function successfully.
Key acronyms and jargon
Most people would agree that IT is full of acronyms and jargon. Business managers should have a sufficient knowledge of the basic acronyms. These include acronyms such as HTML, CMM, ISO, XML, and the like.
There are a number of fundamental aspects of IT that business managers ought to know. While complex aspects are always the domain of IT managers, business managers should take it upon themselves to know at least the IT basics. That is just logical right!?
Photo Credit: Shutterstock



