Handing out sunscreen was the first order of business at this year’s Google I/O 2017 conference. Held in the outdoors Shoreline Ampitheatre in Mountain View, California, this is Google’s largest developer-centric conference of the year. In this article, I cover the big announcements any existing or would-be Google developer should know. Let’s get started!
Announcing TensorFlow 1.2

Google’s TensorFlow product is an open source machine intelligence solution designed to democratize machine learning and artificial intelligence. I pulled the list of new features from the GitHub solution and listed them below. For more information, click here. I have a feeling this list is really exciting to some people, but it goes way over my head. Thinking about this further, I think it is time for me to find a book to learn more about machine learning patterns.
- Added
tf.layers.conv3d_transposelayer for spatio temporal deconvolution. - Added
tf.Session.make_callable(), which provides a lower overhead means of running a similar step multiple times. - Added ibverbs-based RDMA support to contrib (courtesy @junshi15 from Yahoo).
RNNCellobjects now subclasstf.layers._Layer. The strictness described in the TensorFlow 1.1 release is gone: The first time an RNNCell is used, it caches its scope. All future uses of the RNNCell will reuse variables from that same scope. This is a breaking change from the behavior of RNNCells in TensorFlow versions <= 1.0.1. TensorFlow 1.1 had checks in place to ensure old code works correctly with the new semantics; this version allows more flexible uses of RNNCell but can lead to subtle errors if using code meant for TensorFlow <= 1.0.1. For example, writing:MultiRNNCell([lstm] * 5)will now build a 5-layer LSTM stack where each layer shares the same parameters. To get 5 layers each with their own parameters, write:MultiRNNCell([LSTMCell(...) for _ in range(5)]). If at all unsure, first test your code with TF 1.1; ensure it raises no errors, and then upgrade to TF 1.2.- TensorForest Estimator now supports SavedModel export for serving.
- Support client-provided ClusterSpec’s and propagate them to all workers to enable the creation of dynamic TensorFlow clusters.
- TensorFlow C library now available for Windows.
- We released a new open-source version of TensorBoard.
Also announced are new Tensor Processing Units (or TPUs) and the announcement of TensorFlow Research Cloud, that hosts 1,000 TPUs free of charge for those that sign up and receive access from Google.
Google made a lot of Tensor(n), AI, and Machine Learning announcements, so head over and read my article to learn more.
Monetizing Google Assistant with Google Actions
Google Assistant is a product that helps you learn more about people, places, and things around you or just interact with speech or text to perform certain actions. For example, you can set reminders, add things to lists, play music, watch videos, and much more. The assistant is becoming even more prevalent with Google’s new Home product, as you will see in the following video.
[tg_youtube video_id=”VZ9MBYfu_0A”]
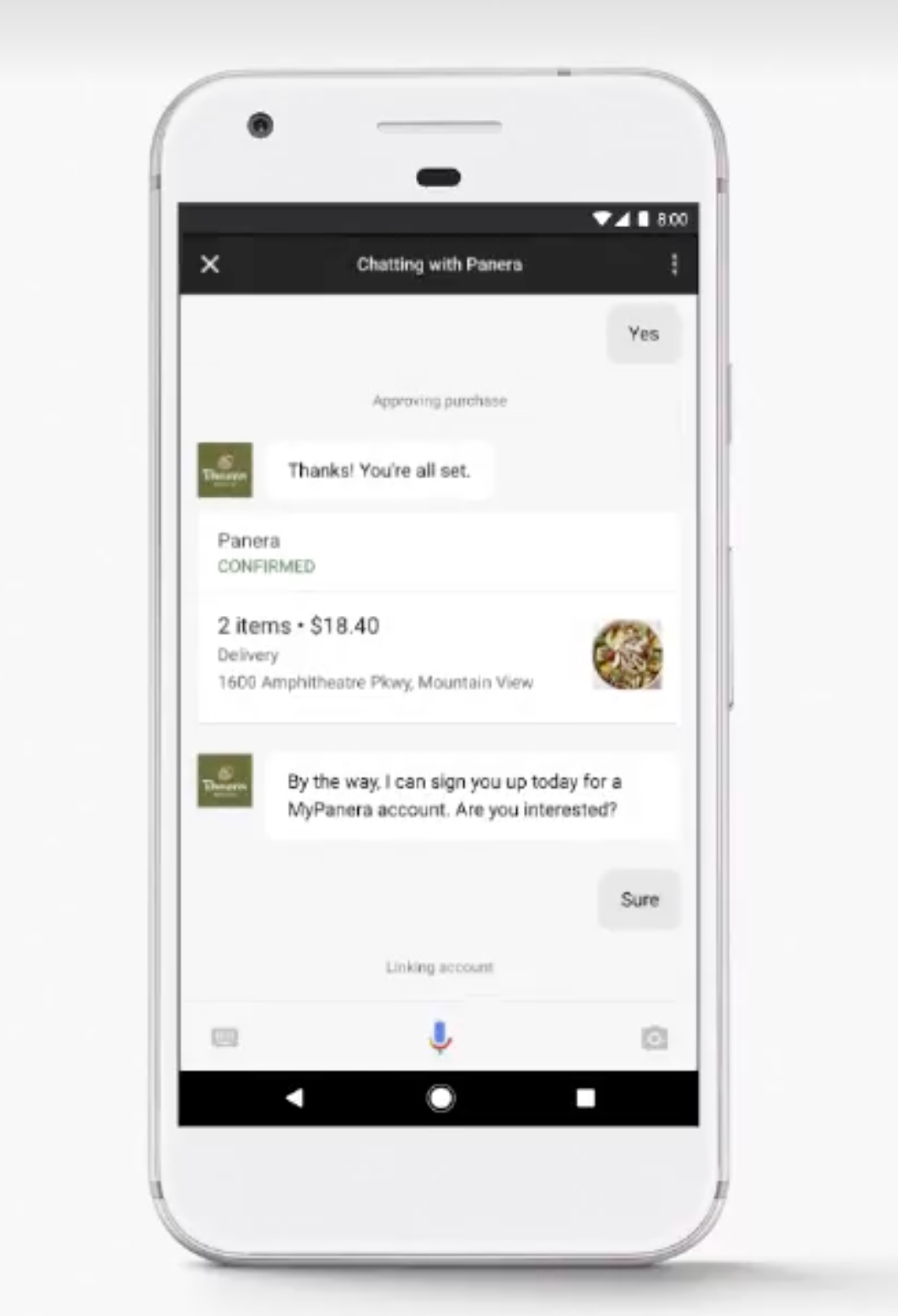
While developers can write solutions for Google Assistant, they have been missing one key element, which is helping those developers monetize their products. The example Google used was searching for lunch. You could ask Google Assistant to find you a restaurant nearby and get a response, but you could not actually find the items you want from the menu and make the purchase.
By creating what Google calls Actions, you can now bring a customer through a full checkout process. Following with the example of finding lunch, Google Assistant can tell you that, say, Panera Bread is nearby. You can then speak or type what you want to order. When you are done building your order, just tell Google Assistant to make the purchase. Once you authenticate the purchase, the order will place and your food will be on the way.
New Google Assistant regions
Later this year, Google Home and Google Assistant will add coverage to the following regions:
- UK
- Canada
- Australia
- Paris
- Germany
- Japan
Android “O”
The upcoming release of Android O is chock full of features that developers will love. Here are the bigger announcements.
Google Play Protect
Google claims to scan over 50 billion apps per day to make sure they are behaving correctly. They also want to make it easy for Android phone users to know their app is not over-utilizing system resources or performing malicious activity. Google Play Protect also provides services that help you find a lost device and blocks potentially harmful websites.

While Google Play Protect is more a user-facing product, developers that may be on the fence supporting Android will be happy to know Google is taking a more proactive approach to protecting their customers.
Of course, with all the data Google Play Protect gathers, they can in turn help developers create higher performance apps.
Introducing Android Studio Profilers
Android Studio is the IDE (integrated development environment) Google recommends you use to build Android apps. Developers do not always know where their code could be more efficient. As you can see in the following image, Android Studio Profilers can track your app’s performance to track down potential problems in your code.
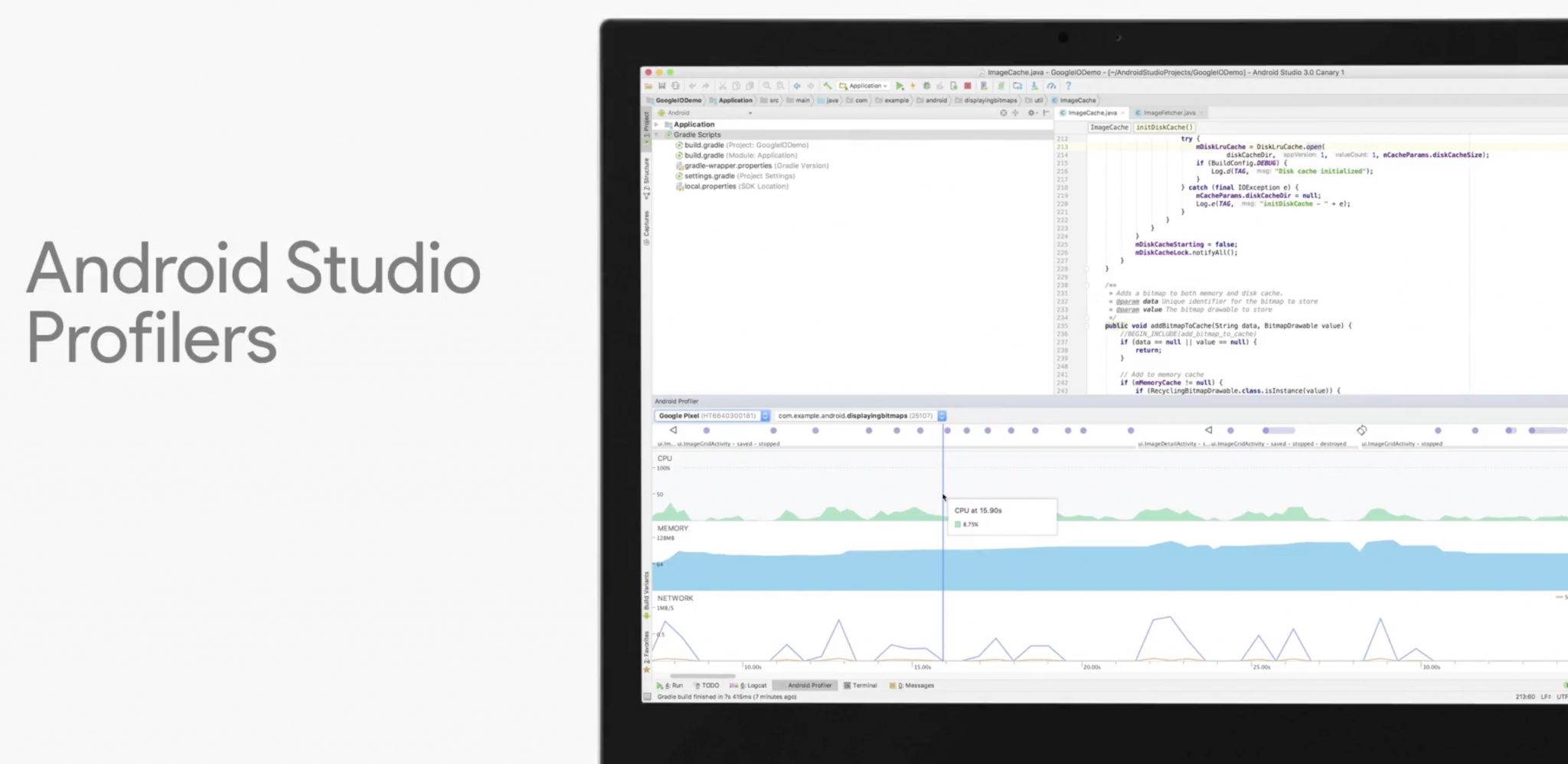
Replacing the older Android Monitor, profilers offer the ability to track the performance of your app on selected devices. There are profilers that allow you to identify issues in CPU, memory, and network activity.
The profiler not only runs in real-time, but you can also record a session and see what function calls are running. This will help you more easily track down what specific code needs fine tuning.
Kotlin as a first-class citizen

If you use Android Studio to create your application, your choices are C++ and Java. That said, many developers prefer to use the Kotlin programming language. Developers can now write their Android Studio apps using Kotlin.
Check out the following image that shows some of the best features Kotlin will bring to Android developers. My favorite feature must be the Elvis Operator. Long live the king?

You may be aware that Kotlin is a product owned and maintained by JetBrains. Google and JetBrains are aware there may be concerns about future support, so they are partnering to turn Kotlin over to a non-profit organization.
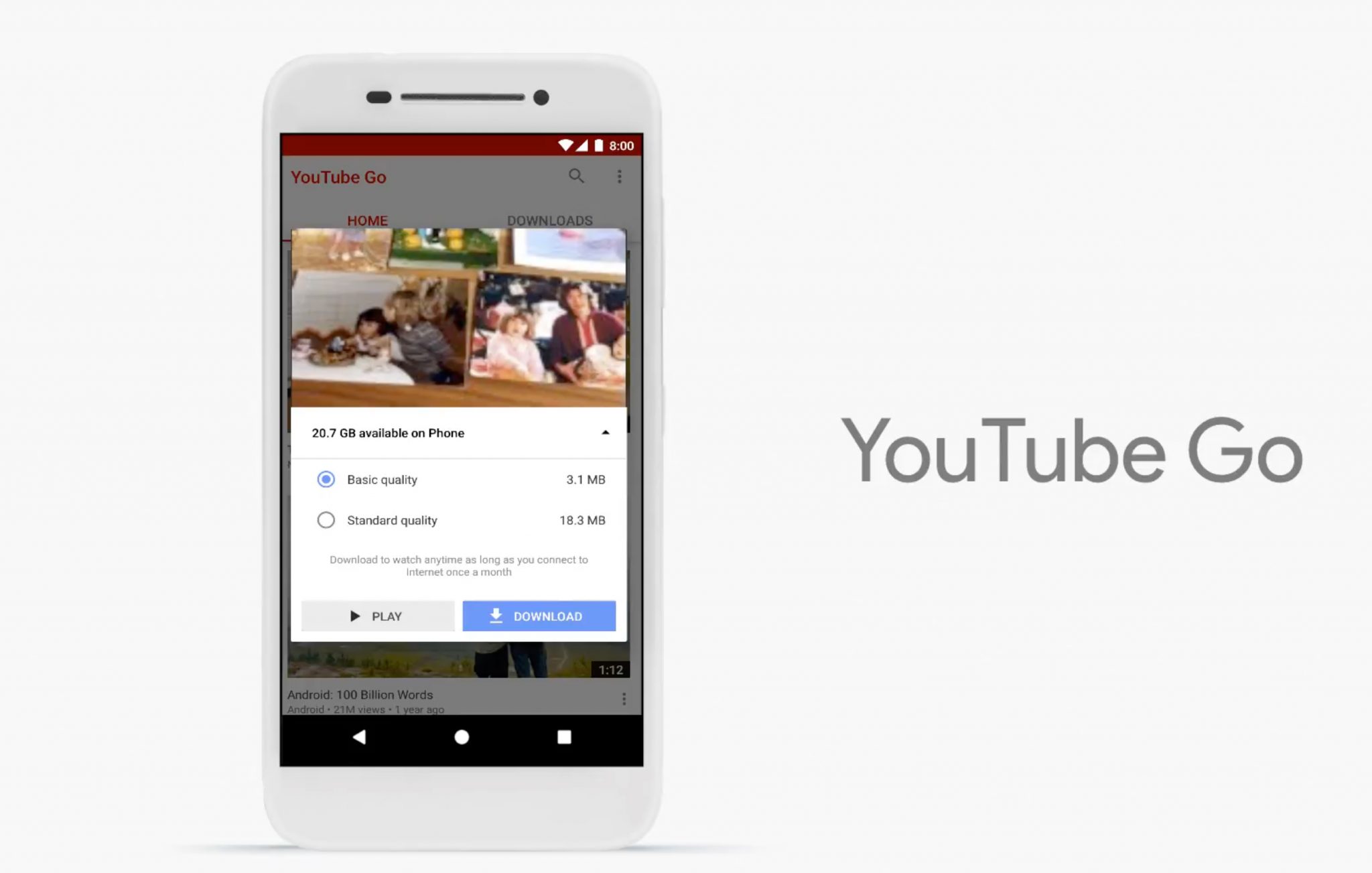
Introducing Android Go
Google announced their Building for Billions initiative, which is focused on capturing the next billion Android users. To do that, they know there will be entry level Android devices with 1GB RAM and minimal bandwidth. With that in mind, Google is essentially forking (my words) Android and creating a slimmer, trimmer, version that compiles down to less than 512MB.
Android Go is much more than a lightweight version of Android though. Developers will have to create APK packages of <10MB in size and carefully tune their apps for network and memory performance.
Developers will not only have to optimize their apps, but may need to prompt users before showing content. As you can see in the following image, the YouTube app for Android Go allows the user to select video quality before playing. The user even has the ability to download the video if they are on a WiFi network so they can play it offline while roaming on their cellular plan.
Android Instant Apps for all developers

Last year, Google announced the introduction of Android Instant Apps. With Instant Apps, a user could, say, visit a website to order food, and then a small piece of your app would automatically download in the background to complete the checkout process.
Unfortunately, Instant Apps were not available for all developers. Now, any developer can create instant apps. Since only certain portions of your app will download, you will have to modularize your app into feature sets. To do this, Google is adding tools to Android Studio that help you do just that. Google estimates it will take a developer 4-6 weeks to modularize an app.
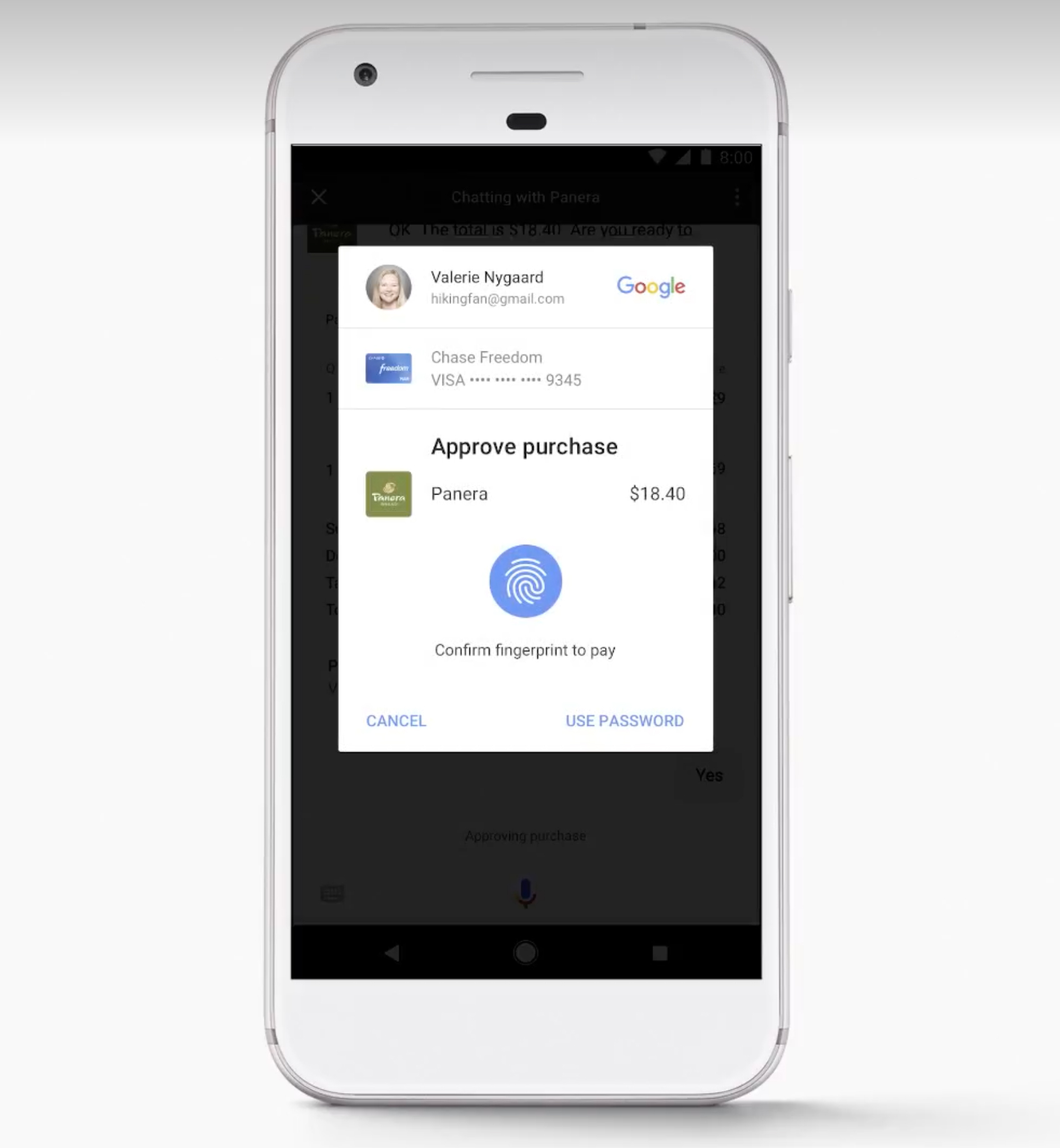
Seamless account linking
Your app probably allows customers to make payments and manage their personal account. If you want your app to work with Google Assistant, then you may require the user to link an existing account so the Assistant works seamlessly for the user.
In the following image, you can see an example where the customer is making a purchase from Panera Bread. Panera asks if the user wants to connect their account. If the user agrees to do so, it will be linked with Google Assistant, making for seamless purchases in the future.
Google says you can also use their own account and identity system so you do not have to build your own.
Google Actions
With all this talk of Google Assistant, you may be wondering how to develop apps for that platform. In order to do that, you need to register actions.
As you can see in the following image, Google recommends you use the api.ai service to define the intent of your app. That example shows that an app’s intent is to help a user book a flight. Google Assistant can then take action by helping the user book the flight through a series of question-and-answer prompts.

Google Chrome
With over 2 billion instances of Chrome out there in the wild, Google is making some investments in this technology to help developers make their sites faster and higher performing.
AMP (accelerated mobile pages)
With AMP, Google is helping to increase the speed at which pages display on browsers. The speed improvements are really significant, so no wonder they have over 2 billion pages using AMP across over 900,000 domains (including ours!)
PWA (progressive web apps)
Google wants web-based developers to get their sites onto the Android home screen by creating PWAs. A PWA is essentially a website that is finely tuned to work on mobile devices. Android users can pin the site as if it were an app to their device. A PWA takes <1MB of space on an Android device because when the user taps the icon, they are automatically brought to the tuned website.
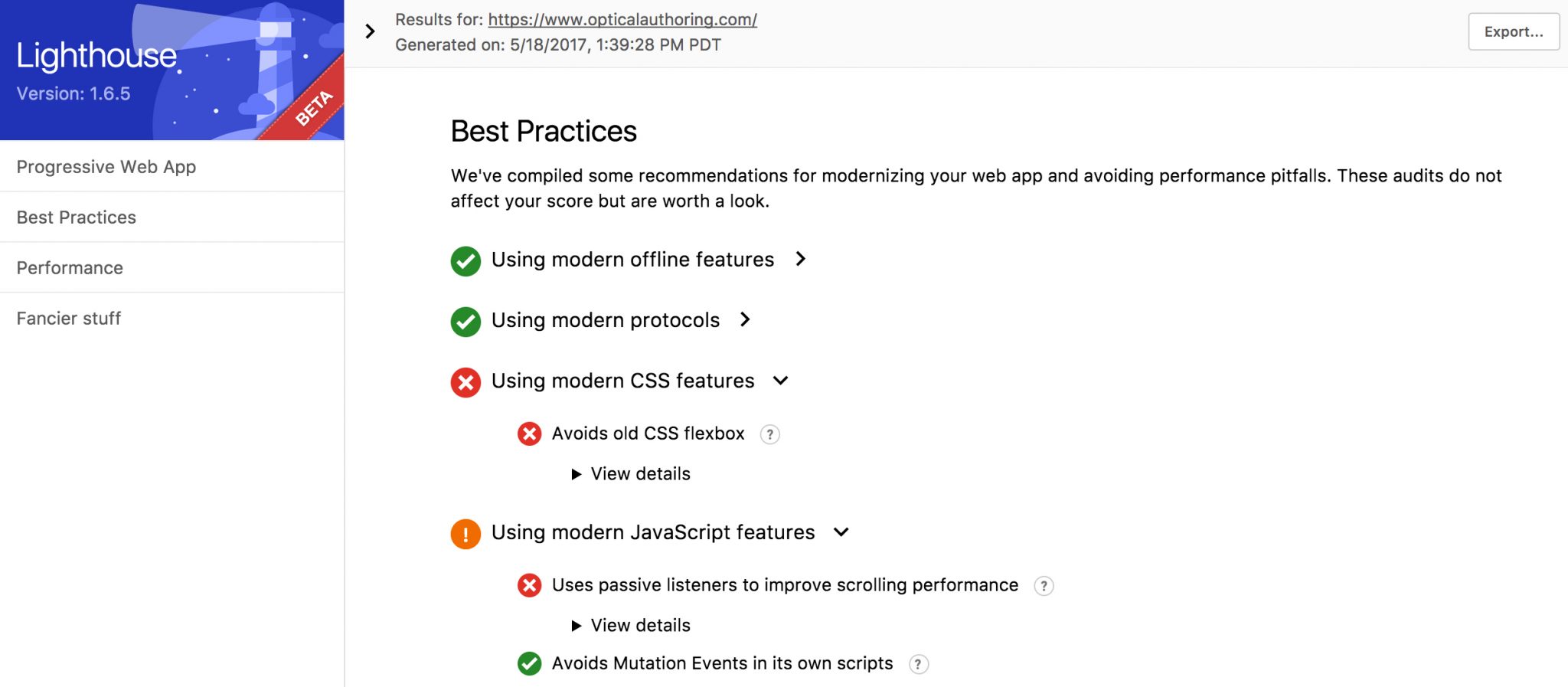
Lighthouse
This Google Chrome add-in allows you to run set of tests against your website to determine if there are any issues, and recommends best practices. I tried running Lighthouse against my own personal website and in the image below, you can see it provides meaningful data that helps you adjust your site for optimal performance.
Firebase

Firebase is Google’s PaaS (platform as a service) that allows developers to create scalable, cloud-based apps.
Functions (serverless computing)
Firebase now supports Functions, which are now all the rage in the new serverless computing market. You can create small bits of code that run a server and perform specific actions.
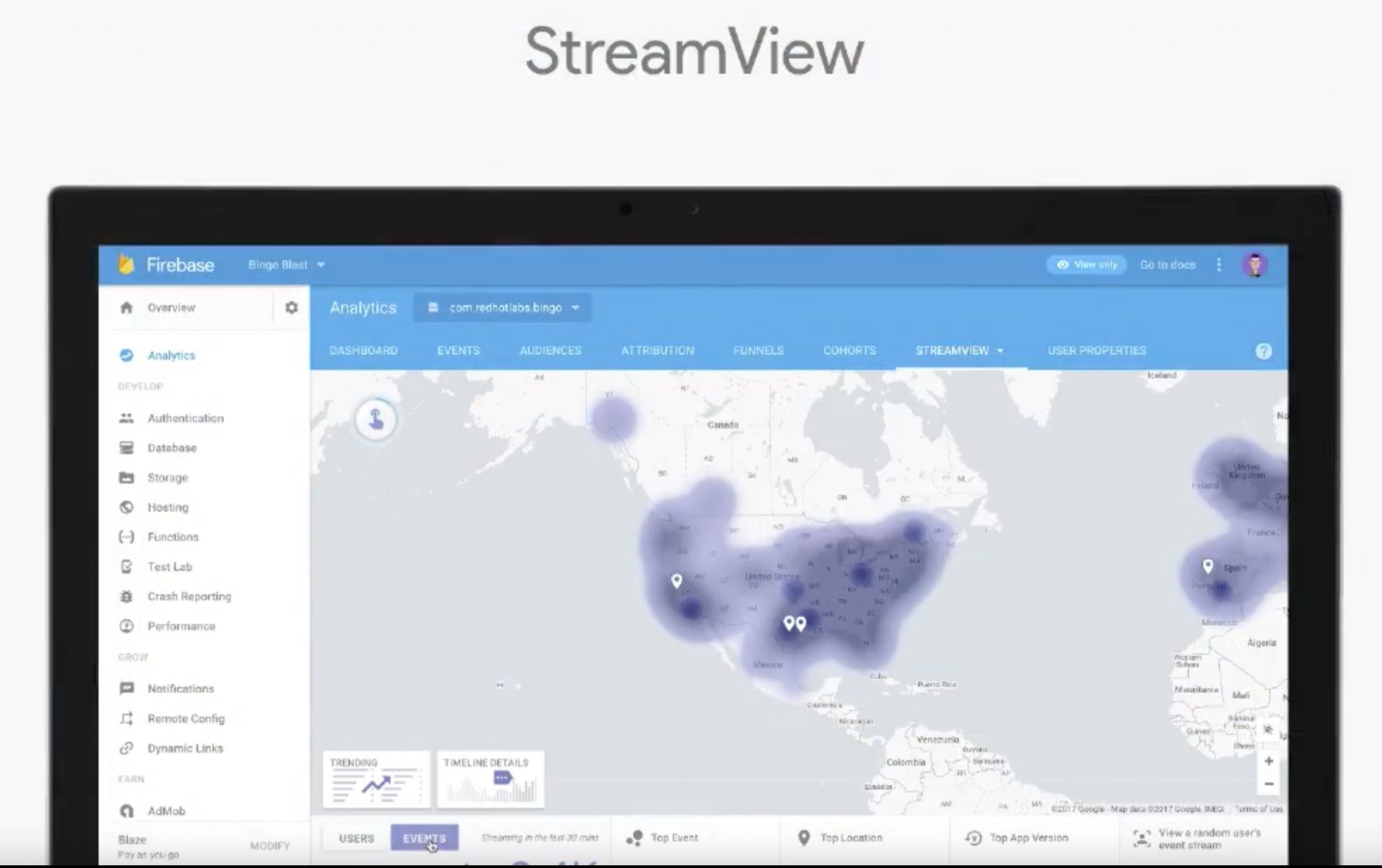
StreamView
StreamView gives you insight into what users are using your app and what they are doing, all in real-time.
There were many more announcements, but these are the most significant for developers. Happy coding!



