SOURCE: Enterprise Storage
Cybercriminals often use an advanced persistent threat (APT) to sustain surveillance or attacks against targets. One of the most valuable assets in a business is its data. Cybercriminals use APTs to steal your information, including trade secrets and patents. Also, bad actors can use APTs to gain employee and client information for extortion or to help better understand your company.
To this end, advanced persistent threats are campaigns against a target where a sustained presence launches surveillance or disruptive attacks. APTs are dangerous as they use advanced techniques to stay undetected. This article discusses what advanced persistent threats are and how to protect your business from bad actors. First, let’s take a look at what an APT is!
What Is an Advanced Persistent Threat?
An advanced persistent threat is a broad term that defines a campaign that uses a series of tools and techniques to gather information and disrupt systems. In short, attackers find an entry into a business, create a beachhead, and attack or surveil over time. The longer they stay in your system, the more information they can collect or the more they can cause disruption.
For APTs to work, they must be able to hide on the target after each operation. It makes advanced persistent threats challenging to execute and requires experienced individuals to do so. Additionally, APTs use advanced tools and techniques that differentiate them from malware.
How an Advanced Persistent Threat Campaign Works
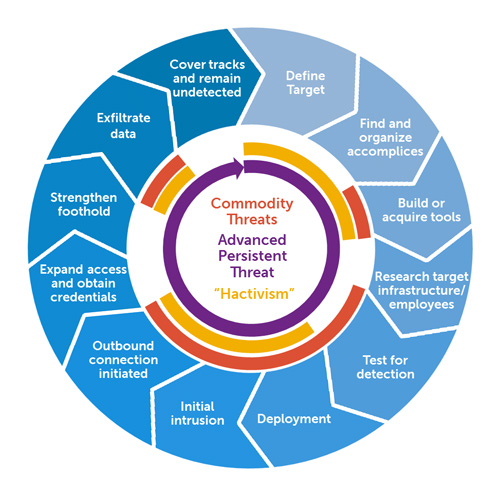
SOURCE: Wikimedia Commons
The image above shows how APT campaigns work. The smallest error can lead an entire APT campaign to fail. Unless you work in a high-value target or supply chain, you’re unlikely to see APT campaigns in the wild.
Some advanced persistent threats can be added across entire supply chains using one compromised vendor. Bad actors then wait for complete saturation of the supply chain to harvest data or cause disruption. You often find governmental-level intelligence teams using advanced persistent threats for both activities. Attacks on infrastructure are a common method to reduce the GDP of the targeted nation. Or, governments use it to gain intelligence on secure sites. To do this, teams target third-party solution vendors to add APTs to critical industries. This is often through modifying software without the vendor’s knowledge before installation.
Bad actors start once a backdoor is established. Alternatively, they use automated attacks for many targets. Manually performed procedures work better than a generic approach. When investigating an attack, if you spot generic attack methods, you know you’re not the only one in the firing line. To help others in your sphere, you should also warn them about the risk of an APT.
Remember, attackers often want more than just your data. They want your business partner and client data. You can expect an APT attempt to infiltrate your entire network and others around you. When you start seeing suspicious activity across your infrastructure, you might have an advanced persistent threat on your hands.
So, how do you know if you’re under attack? Let’s turn our attention to the 5 stages of an APT attack. Identifying these stages can help you spot when you’re under attack.
5 Stages of an Evolving Advanced Persistent Threat Campaign

SOURCE: Flickr
Advanced persistent threats are custom-made and use advanced techniques, but they all follow the same 5 stages. Knowing these 5 stages helps you assess threats and neutralize them.
1. Gain Access
Attackers often use attacks like spear-phishing and SQL injections to gain access to your network. If you have a well-trained staff that practice good common sense, the attacker will have to work harder to gain access. Additionally, consider using an integrated all-in-one cybersecurity solution and network management tool to reduce attack surfaces.
2. Establish a Foothold
After step 1, you can expect the attackers to add a backdoor to access your network. Backdoors need the necessary permissions and connections to work. Check your network egress traffic for strange remote access connections. Be aware that bad actors can use stolen hardware or spoofed MAC addresses to fool you. Be on the lookout for new holes in your firewall or open ports used by the bad actor during this process. Follow IP address management and remove outdated hardware from your network.
3. Deepen Access
Once they have a backdoor, you must watch for signs of privilege escalation. Attackers use this to get better access to the system. Be on the lookout for new administration accounts or ones used outside office hours. At this stage, cybercriminals can change access control levels (ACLs).
4. Move Laterally
As the attacker gets more access, they’ll add customized software to your infrastructure. This can be monitoring and collection software and attack software that compiles once triggered by the attacker. Additionally, attackers will try to map out your network at this stage.
5. Look, Learn, and Remain
The last step of an APT is using attacks to help extract data from your network. Additionally, attackers will try to ensure they remain hidden so they can repeat the process. Repeating this process allows these bad actors to keep stealing your sensitive data. To this end, it takes a lot of upfront effort to craft an APT to suit this type of espionage. If you find the APT early, you could harden your systems. As a result, your attacker will need to start with a new plan.
Now that you know APTs are highly customized campaigns, let’s look at the characteristics of an ATP attack. In addition to knowing the stages of an ATP attack, knowing the common characteristic of one will also help you to spot if you’re under attack.
Characteristics of an APT Attack
APT attacks are not easy to spot; why? Because advanced persistent threats hide their existence from you. If you know of common attacks that can breach your network, look for signs of these. Moreover, you know attackers need a backdoor to conduct operations for manual attacks. Check for connections to remove machines your business wasn’t connecting to before.
Seeing the signs of being out-maneuvered in the marketplace often tells you that either you have an APT campaign targeting you or a mole. You’ll know the difference if you start finding your servers going down or services falling offline. Use GFI’s Exinda or a similar solution that maps and identifies the quality of service to help check for inconsistencies in your system.
Checking transaction logs may help if you know the time of the attack. You might find a computer on your network connecting to the server or a remote connection. Advanced persistent threats hide their tracks, and the bad actor might have deleted your logs. If so, check earlier images and backups for any traces.
You’ve learned all the ways to spot if you’re under an ATP attack, but how can you protect your business against them? Read on to discover what you can do to protect your business from APT campaigns!
Quick Steps to Help You Protect Your Business
APT campaigns need to target critical parts of your business. To mitigate APT campaigns working effectively, use the following steps:
- Patch all software as soon as patches are released.
- Use encryption for all network connections to stop bad actors from sniffing your data packets.
- Filter emails to remove spam and reduce phishing attacks.
- Enable security logging and push notifications to help detect nefarious actions.
- Regularly screen user lists and remove old users.
What You Can Do to Check for APT Campaigns

SOURCE: Pexels
Check your firewall for changes along with your antivirus solution settings. Remember, bad actors need to move around and map your system. You also need to check permission escalations and ACLs. Additionally, search for new administrators or superusers. If you find one, compare it to your database, active directory, or LDAP. Using a unified threat management software solution can also help speed up the process of finding APT threats.
Finally, check your whitelisting of domains hasn’t changed. Whitelisting is the flawed security measure of adding domains to a file. You often only create whitelists during platform installations; if it’s changed, check the date so you can investigate more.
Now let’s wrap up!
Final Thoughts
APT campaigns are rare due to the specialist expertise needed to design, develop, and execute them. Cybercriminals work in teams, like a modern business, to handle each stage of the process. Still, the cost of producing an effective APT means you’ll only find elite teams using them. Finding advanced persistent threat operations on your network is challenging. However, you can discover attackers by checking for backdoors, new or modified users, and permission escalation.
The National Security Agency (NSA) uses similar tools for the infiltration and surveillance of criminal organizations. The NSA website provides free tools for security experts looking for real-world examples to test systems. In short, white and black hats know these tools, so the NSA no longer need to hide them. Instead, NSA releases this software to help train you against the black hats.
Check out the FAQ and Resource section below to learn more about advanced persistent threats and related topics!
FAQ
What are penetration testing tools?
Cybersecurity experts use penetration testing tools to test if the network can withstand attacks. These tools test your security systems, attempting to attack several aspects of your network to find exploits to fix.
How many different types of malware do I need to be aware of?
You’ll find only a dozen types of malware in the wild. Bad actors create different variants and hybridize malware to get around security measures. But, new hybrids of malware are always appearing every day, so antivirus systems need to stay up-to-date to combat this.
How long do advanced persistent threat (APT) campaigns last before detection?
APT campaigns can last for a very long time before the attacker reaches their final goal. You can expect 3 to 4 months of positioning software and mapping your network before bad actors finish. It gives your cybersecurity team time to use unified threat management strategies to reduce your risk of escalation.
Do cybercriminals use software to deploy APT campaigns?
Yes, some APT campaigns currently use Office 365 to gain entry. You often find specialist platforms implemented by third-party vendors used as a carrier for APT software. This can target a specific company, supply chain, or whatever business comes into contact with the software.
What is an indicator of compromise (IoC)?
An IoC is something a cybercriminal leaves behind, giving clues on how their attack works. These can be things like log files or zip files. You can use this to assess an attacker’s final goal if the attack is in progress. This enables you to preempt the attack, stop it, and reduce damage.
Resources
TechGenix: Article on Web Filtering
Learn how web filtering can help you protect your business from APT campaigns.
TechGenix: Article on the Different Types of Firewalls
Discover the different types of firewalls and what they can offer your business.
TechGenix: Article on InfoSec Overload Syndrome
Find out how InfoSec overload syndrome can be mitigated.
TechGenix: Article on Proxy Servers
Learn how proxy servers can protect your business from cyber threats.
TechGenix: Article on Linux VPNs
Discover the best Linux VPNs for your business.



