Source: madartzgraphics on Pixabay
Do you know what your most sensitive data is? What about who has access to it or where you stored it? You can’t protect your data effectively without answering these questions. Cybercriminals are always trying to find ways to steal this valuable data. For instance, an attack involving the theft of credit card details could lead to severe financial and legal complications. On the other hand, information that’s already public, such as your website’s content, doesn’t pose much of a risk. Keeping track of security risks can be challenging when you have a large volume of data. This is where having an effective data classification policy becomes essential!
In this article, I’ll explain what a data classification policy is, how to create one, and how to implement it in your company through two methods. Let’s start with a definition.
What Is a Data Classification Policy?
A data classification policy is a detailed plan for handling confidential data. To clarify, it identifies different sensitivity levels, access rules, and storage procedures for your data. As a result, anyone in your company can use the policy to identify and store sensitive data securely. Specifically, this policy provides a framework for you to:
- Catalog all your data for cybersecurity
- Determine the risk of exposure for any data class
- Prevent security loopholes by ensuring everyone handles highly sensitive data consistently
- Avoid wasting resources to protect data that isn’t important
A data classification policy ensures that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data. It mitigates the risk of data loss as well as security breaches. Let’s understand the concept in more detail by looking at how to create one!
How to Create a Data Classification Policy
Source: geralt on Pixabay
A data classification policy has 5 key sections, which I’ve outlined below. I also included some examples below each section that you can refer to.
1. Objectives
The objectives define the motivation and benefits of data classification for your company. You can explain your purpose at the beginning to inspire employees to implement it.
Example
“The data classification policy aims to ensure that our high service standards extend to our customer’s data. By securing their data, we strengthen customer and investor trust. We also meet regulatory compliance requirements.”
2. Scope
The scope outlines what data the policy extends to and who must follow it.
Example
“This policy governs all our organizational data, both digital and physical. It covers any data that enters our IT systems from our communication channels and applications. It also includes digital documents that our employees create within the organization. All employees, vendors, and contractors must follow the data protection procedures outlined below.”
3. Roles and Responsibilities
Next, your policy should outline data protection’s broad functions and responsibilities. You can also identify the teams or individuals carrying out those roles.
Example
“Three key roles responsible for implementing this policy are:
- Chief Security Officer: Responsible for approving future policy document changes
- Policy Manager: Responsible for ensuring all teams implement the policy. Policy managers will perform regular audits and provide implementation support
- Data engineer: Responsible for configuring data protection software and tools.”
4. Classification Categories
Next, you should outline and define the data classification categories. You can also explain how to determine the category for new data in the future.
Example
“Our data classification levels are:
- Restricted: Any intellectual property that constitutes trade secrets
- Confidential: Any data that contains personally identifiable information like name, address, phone number, or financial information
- Internal use: Any operational data that is more than two years old
- Public: Any data that is already in the public domain
If your data set fits in more than one category, please assign it to the higher category. For example, data that is more than three years old and contains personally identifiable information is confidential and not internal use.”
5. Data Classification Policy Table
Your data classification policy should include a table that identifies each data asset, its classification, definition, type, and impact. This table should be comprehensive and cover all significant data sets. In essence, this table is the main part of your data classification. I’ve provided some basic example tables below.
Example 1: Healthcare Sector
Organizations within the healthcare sector must comply with HIPAA regulations. A data classification policy for a state hospital can take the form below:

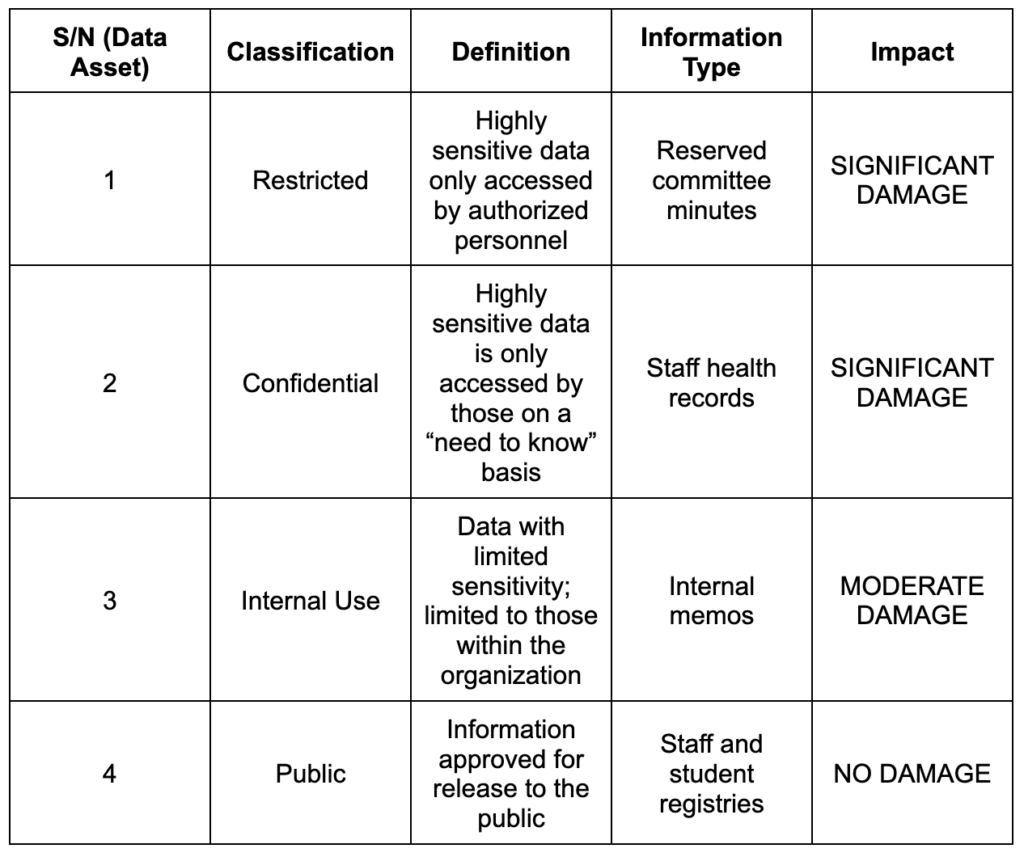
Example 2: Education Sector
A data classification policy for a public university may take the form below:
The above examples merely provide a general view of a data classification policy. In practice, these policies are much more detailed. For instance, they might include technical specifications for an organization’s IT systems. Additionally, they might include details like password policies and network and database configurations. You can also add a glossary defining any technical terms.
Once you’ve created a data classification policy, you must ensure everyone follows it. The right implementation is key here. Let me now share two methods of effectively implementing a data classification policy.
How to Implement a Data Classification Policy

Source: Michael Buckbee on Varonis
As previously stated, you can implement a data classification policy using 2 methods: user-driven classification and automated classification. Let’s look at each of them in more detail, along with their respective pros and cons.
1. User-Driven Classification Method
The user-driven classification method puts the data users in charge of classifying and labeling acquired data. For example, your marketing team can classify advertising reports, while your operations team can classify production data. Team managers will also enforce policies and restrict overall data access in the team.
Pros
The user-driven classification method is very accurate since the user uses the data in daily activities. This method also takes advantage of the user’s knowledge of context. Therefore, you’ll have minimal errors as data classification is more sensitive and specific.
Cons
The process can be slow and time-consuming. Also, personnel may resist the additional workload as it’s not part of their core responsibilities. You also risk having team members not take the data classification policy seriously. As a result, they may miss out on implementing certain details. Consequently, this can lead to them creating a security loophole.
2. Automated Classification Method
This approach uses software solutions to implement policies and perform classification tasks. The software also uses machine learning (ML) technology to analyze keywords within each data content. It can automatically place each file in its proper class based on the detected phrases. In addition, you can restrict file access based on the classification. One popular automated classification tool is Spirion’s Sensitive Data Platform.
Pros
Automated classification is extremely beneficial in classifying non-user-generated data, such as enterprise resource reports. It also helps in dealing with easily-identified personal information like credit card details.
Cons
Despite their numerous use cases, automated solutions have their drawbacks. First, they often create false-positive classifications. This results in unnecessary security protocols for non-valuable data, causing resource wastage. They may also create false-negative classifications. These results can lead to the loss of sensitive information and regulatory compliance violations.
It’s time for a recap of everything you’ve learned so far!
Final Words
To conclude, a data classification policy provides a framework for companies to classify their data. Having one in place is a crucial first step in ensuring data security. It provides visibility into the nature, availability, and accessibility of data in your company. It also helps you meet compliance regulations and industry best practices.
Designing a data classification policy requires careful thought. You must first define the objectives and scope of your policy. Then you must consider aspects like personnel responsibilities and classification categories. After creating one, you must take measures to implement the data classification policy across your company correctly. You can use a user-driven or automatic classification method for proper implementation.
Do you have more questions about data classification policies? Check out the FAQ and Resources sections below!
FAQ
Which companies need a data classification policy?
A data classification policy is critical for companies across all sectors. Every company deals with sensitive data and personal information about customers and employees. You also have to consider the regulatory frameworks that guide data handling in different sectors. Thus, companies need a data classification policy to comply with these regulations.
Why should my company have a data classification policy?
A data classification policy offers the structure to protect your company’s data. Specifically, it allows you to evaluate the risks to sensitive data, and you can use this information to handle this data to minimize those risks. Implementing a data classification policy gives you visibility into your data’s nature, location, and integrity. Overall, you can save money and time by prioritizing protecting high-impact data.
What are the best practices for creating a data classification policy?
Firstly, identify clear security goals behind your data classification policy. Your objectives will motivate everyone to implement the policy. Secondly, create distinctive classification labels and uniform guidelines. Maintain consistency throughout the company. This helps to avoid confusion and security mistakes. Finally, conduct a thorough regulatory and legal assessment of the data classification process.
What is the GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a set of European data standards. Overall, these standards assist companies in handling sensitive data carefully and respectfully. Companies can face severe penalties if they don’t abide by the GDPR. Therefore, companies must implement rigorous data classification policies. The GDPR mandates businesses to assign particular security controls to data. In turn, these controls help prevent unauthorized exposure.
Who should be in charge of data classification?
Every company should have one or more data stewards who will place data in their appropriate classes. Essentially, the data steward is a senior-level employee that oversees the life cycle of one or more data sets. This individual oversees the awareness, accessibility, and release of data. They also handle the appropriate use, security, and management of data.
Resources
TechGenix: Newsletters
Subscribe to our newsletters for more quality content.
TechGenix: Article on Data Protection and Security
Explore some top tips and best practices for data security within your organization.
TechGenix: Article on Data Classification for Compliance
Read about the benefits, challenges, and best practices of data classification.
TechGenix: Article on Cloud Data Loss Prevention
Learn more about cloud data loss prevention and why your company needs it.
TechGenix: Article on Data Leaks
Discover more information about data leaks and how to prevent them.
TechGenix: Article on Data Lifecycle Management
Find out what the best policies and procedures for data lifecycle management are.



